VirtualBox 7 is a popular virtualization software that allows users to run multiple operating systems on a single physical host. With its latest release, VirtualBox 7, users can now take advantage of even more features and enhancements.
This guide will show you how to install VirtualBox 7 on Linux Mint, a Ubuntu-based Linux distribution known for its user-friendliness, reliability, and great support. So, whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, this guide will provide the steps to set it up on your Mint system successfully.
VirtualBox is available for installation from the Linux Mint 21 “Vanessa” repositories, but the version is 6.1. However, VirtualBox 7 was recently released, and it offers significant advantages over its predecessor, such as:
- Full virtual machine encryption support
- Support for UEFI SecureBoot and TPM 1.2/2.0
- Enhanced 3D support
- Automated virtual machine builder
- Integration with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
Fortunately, there is an effortless way to install VirtualBox 7 on Linux Mint, which we will show you in this guide.
The tutorial will use the sudo command and assuming you have sudo privileges.
Step 1: Import VirtualBox’s Repo GPG Key
VirtualBox 7, as previously stated, is not available in the Linux Mint 21 repositories. So, we’ll add it to our Mint system. But first, import the Oracle VirtualBox GPG keys that sign the software.
Open the terminal and run the following command:
wget -O- https://www.virtualbox.org/download/oracle_vbox_2016.asc | sudo gpg --dearmor --yes --output /usr/share/keyrings/oracle-virtualbox-2016.gpgCode language: JavaScript (javascript)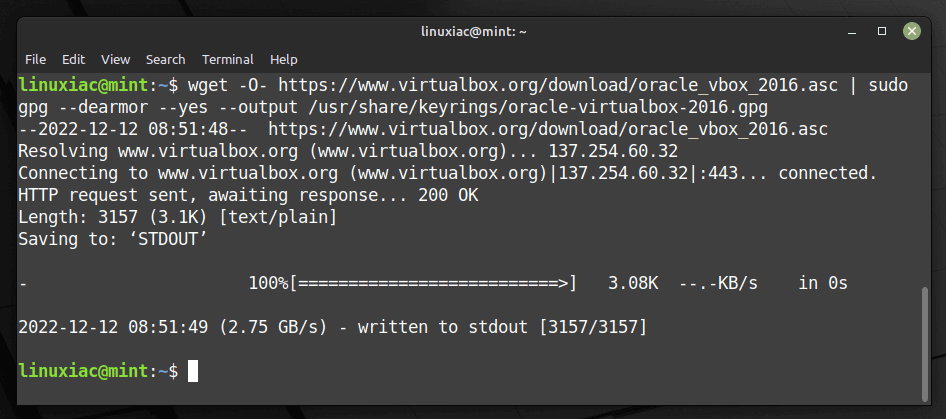
We can now proceed to import the official VirtualBox repository.
Step 2: Add Official VirtualBox Repository
After importing the GPG keys, we’ll add the official VirtualBox repository to our Linux Mint system. This implies that the update package will be made available with the rest of your system’s regular updates if a new version is released.
echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/oracle-virtualbox-2016.gpg] http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/debian jammy contrib" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/virtualbox.listCode language: PHP (php)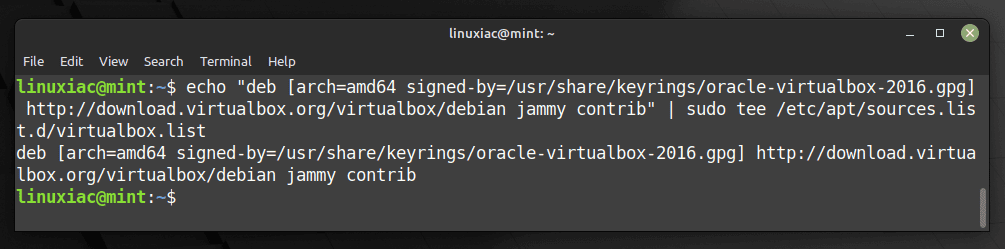
Step 3: Run System Update
Before we proceed with VirtualBox installation on our Linux Mint 21 system, we should refresh the packages list to make the system aware of the newly added VirtualBox repository’s packages. So, run the below command to update the APT repositories index.
sudo apt update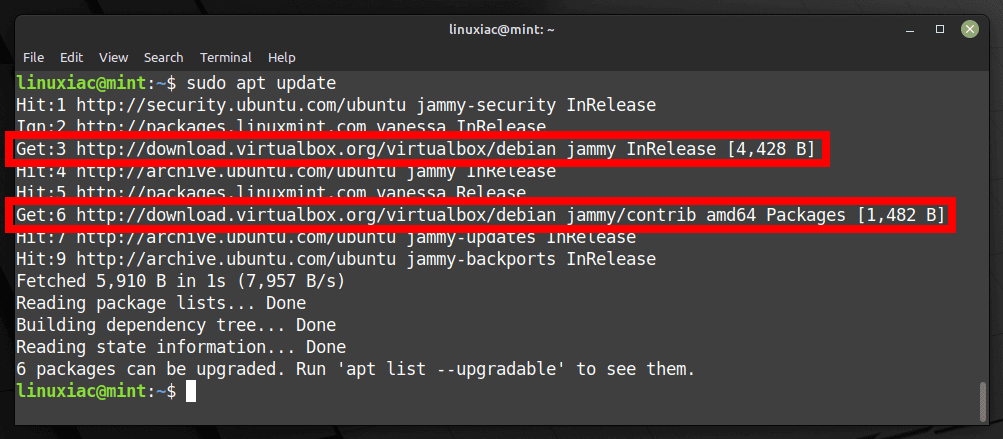
As you can see from the image above, our new VirtualBox repository is now available and ready to be used.
Step 4: Install VirtualBox 7 on Linux Mint 21
Everything is already prepared for the actual installation. Now, to install VirtualBox on Linux Mint 21, run the following commands:
sudo apt install virtualbox-7.0Code language: CSS (css)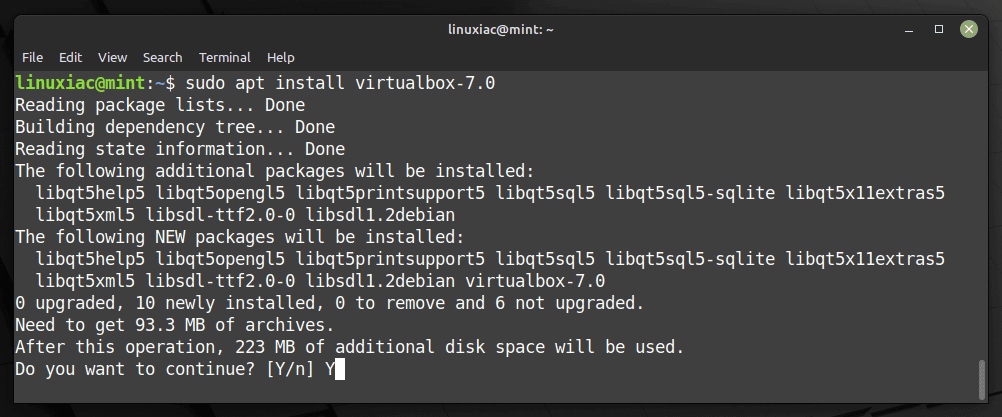
Wait for the installation to complete. The VirtualBox is now installed and ready to be used on your Linux Mint 21 system.
Step 5: Install VirtualBox Extension Pack
This is an optional step, but I strongly encourage it because it will make working with VirtualBox on your Ubuntu system easier and more convenient. VirtualBox Extension Pack unlocks many great features, such as:
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) integration
- VirtualBox Remote Desktop Protocol (VRDP)
- Host webcam passthrough
- Disk and full VM encryption
Let’s highlight one peculiarity here. The installed VirtualBox Extension Pack’s version is highly recommended to match the version of VirtualBox installed on your Ubuntu 22.04 system.
So, to verify the exact version of the installed locally VirtualBox, you can use vboxmanage, a build-in VirtualBox’s command:
vboxmanage -v | cut -dr -f1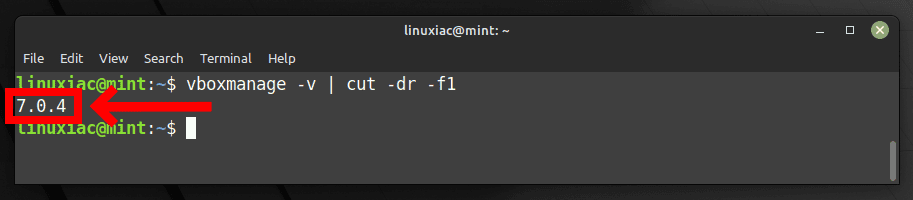
As you can see, the version of Virtualbox installed is 7.0.4. Therefore, you must then download the Extension Pack with the same version.
However, if your VirtualBox installation version is different, replace both places containing 7.0.4 in the command below with the actual version. In addition, you can also go straight to the downloads page and look at the available versions.
wget https://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/7.0.4/Oracle_VM_VirtualBox_Extension_Pack-7.0.4.vbox-extpackCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Next, to install the VirtualBox Extension pack, run the vboxmanage command as follows:
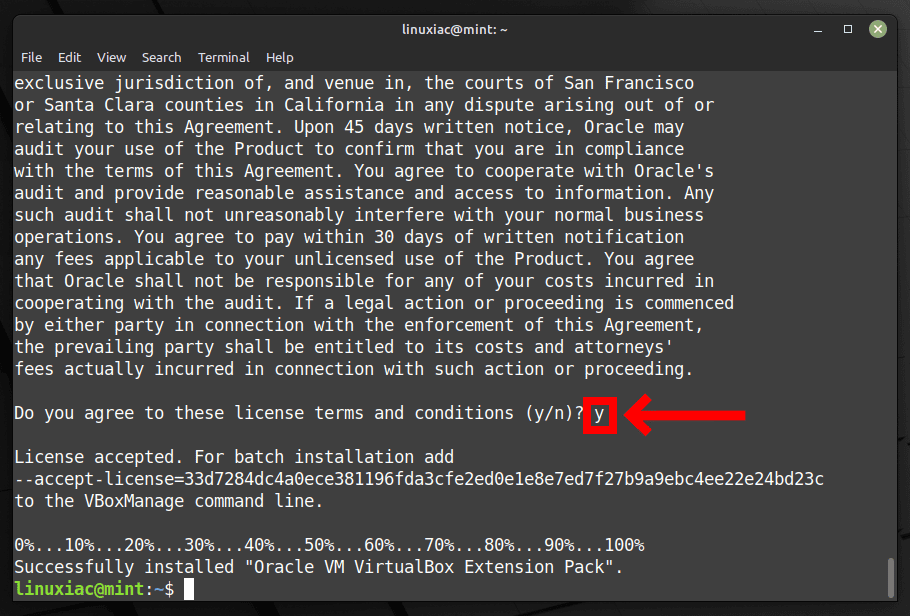
sudo vboxmanage extpack install Oracle_VM_VirtualBox_Extension_Pack-7.0.4.vbox-extpackCode language: CSS (css)You will be prompted to agree the Oracle’s license terms and conditions. So, type “y” to confirm and press Enter.
Additionally, you can verify installed VirtualBox’s extension pack version by running the following:
vboxmanage list extpacksCode language: PHP (php)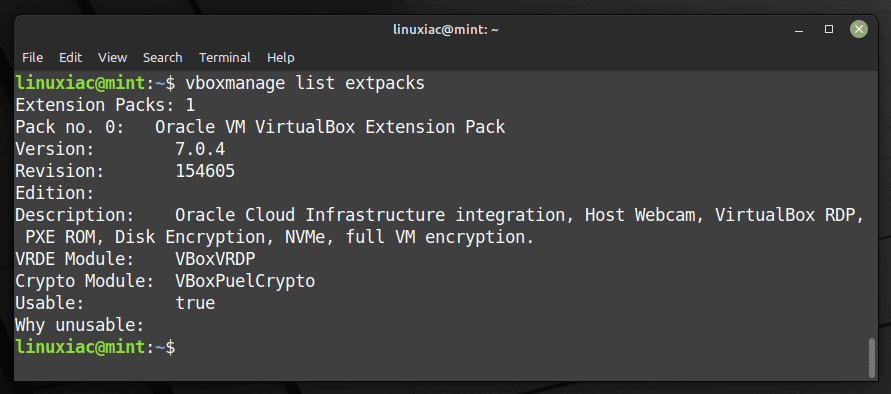
Step 6: Add User to vboxusers Group
Before using VirtualBox, you should add your user account to the vboxusers group. This is quick and simple to accomplish by running:
sudo usermod -a -G vboxusers $USERCode language: PHP (php)Now perform a reboot. After login, check that you are in the vboxusers group with this command:
groups $USERCode language: PHP (php)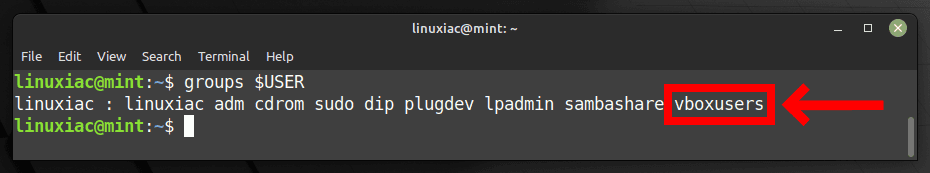
Step 7: Running VirtualBox on Linux Mint 21
You can start using VirtualBox by launching it from the Linux Mint start menu.

Conclusion
That concludes our guide on installing VirtualBox on Linux Mint 21. We hope you find this guide helpful. Thanks for your time!
We recommend checking the official documentation for individuals who want to learn more about the features offered by VirtualBox and how to use them effectively.
Finally, you can use VirtualBox in an entirely headless mode to turn your server into a virtualization environment. To learn more about utilizing this VirtualBox feature, check out our guide: “How to Setup and Manage VirtualBox VMs on a Headless Server.”
Thanks for using this tutorial. Your feedback and comments are most welcome.
