Debian is one of the most reliable, secure, and stable Linux distributions, ensuring your server’s seamless operations. Because of these qualities, it is a reasonable and often favored choice of system administrators for Linux-based servers.
The LEMP software stack consists of a group of server-side software that serves dynamic web pages and web applications. It is an acronym representing four separate components: Linux OS, Nginx Web Server, MySQL/MariaDB Database, and PHP Scripting Language.
This tutorial shows you how to install Nginx, MariaDB, and PHP on Debian 11 (Bullseye), transforming it into an ultimate server for developing and hosting your web applications. So without further ado, let’s get to work.
Prerequisites
You’ll need access to a Debian 11 server to complete this guide. In addition, all commands in this tutorial are run by a regular user with sudo execution abilities. Therefore, you should own one.
Of course, you can skip the sudo portion of the commands and run them directly as a root user. The result will be the same in both cases.
Furthermore, ensure that your firewall does not block port 80 to the server and port 443 if you plan to use SSL.
1. Update Software Repositories
First, we will use the APT command to update the list of available packages. This ensures that only the most recent versions of the packages are used throughout the installation of the LEMP stack on our Debian 11 system and prevent difficulties.
In addition, make sure the system is fully updated. If packages are waiting to be updated, I advise applying them before moving on.
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
2. Install Nginx Web Server on Debian 11
The web server enables you to serve content such as web pages to website visitors. This step takes care of the second requirement in the LEMP stack, the Nginx web server.
Use the following commands to install the latest Nginx version on your Debian 11 server. When prompted, enter “Y” to confirm that you want to install it.
sudo apt install nginx
After complete installation, the Nginx web server will be up and running on your Debian 11 server. But, first, let’s check if it works as expected.
Open a web browser on your system and type the server’s IP address in the address bar.

The system should display the Nginx welcome page.
3. Install MariaDB Server on Debian 11
Now that you have a working web server, you need to install the database server to store and manage data for your website. Instead of MySQL, we’ll be installing MariaDB in this tutorial.
It is an open-source RDBMS (Relational Database Management System), backward compatible, binary drop-in replacement of MySQL. MariaDB provides improved performance with faster replication speeds, tighter security measures, and additional storage engines compared to MySQL.
To install the MariaDB database, run the commands below, and when prompted, confirm installation by typing “Y” and hitting “Enter.”
sudo apt install mariadb-server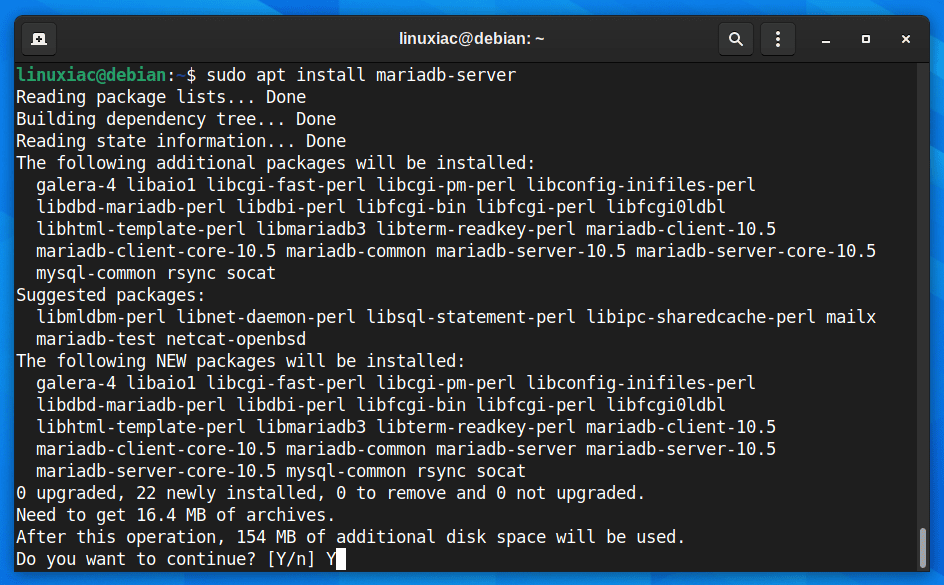
3.1 Securing MariaDB Server
Next, we’ll use a script (mysql_secure_installation) provided by the mariadb-server package to restrict access to the server and remove unused accounts because the default setup makes your MariaDB installation unsafe.
Run the post-installation security script.
sudo mysql_secure_installationAfter running the above command, you will be prompted to enter the MariaDB root password. Just leave the root password empty, and press the “Enter” key. For the rest, keep typing “Y” and hitting “Enter.”

Great! You have secured the MariaDB server in the LEMP stack on Debian 11.
We clarify that the password specified above for the MariaDB root accounts is only for remote users. To log in from the host we installed, you do not need to enter a password and will not be asked for one. Just type “sudo mysql” to access the MariaDB shell.
3.2 Testing MariaDB Installation
Let’s log into it and run a simple query to check if the database server is functioning normally.
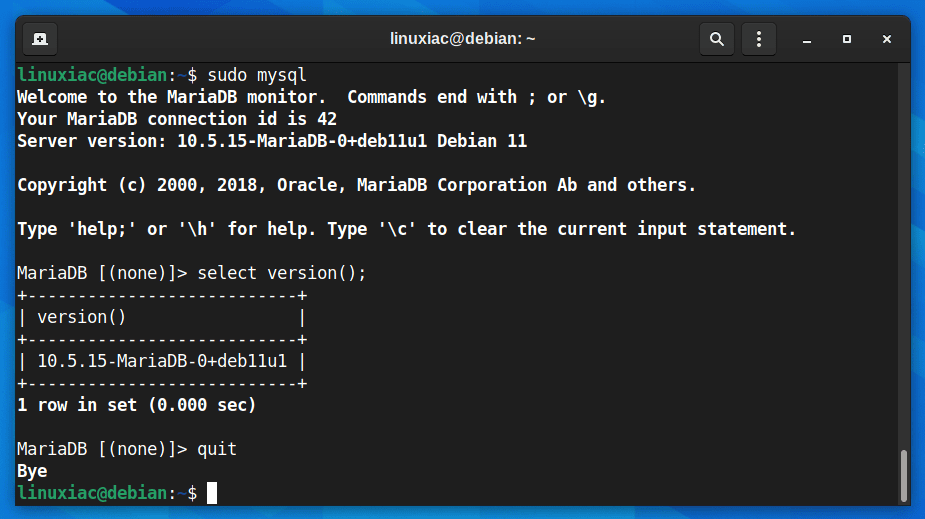
To log in, type the command shown below.
sudo mysqlThis will connect to the MariaDB server, and the MariaDB shell should come up. Then, run a simple query:
select version();In response to your query, the MariaDB server should return its version. Finally, to exit the MariaDB shell and return to the system terminal, use the “quit” command.
4. Install PHP on Debian 11
The last step to have a complete LEMP stack installed on our Debian 11 “Bullseye” system is to install PHP Scripting Language. To add PHP support to Nginx, you must install and use PHP-FPM to execute PHP files.
So, to install PHP-FPM and several most widely used PHP modules, type the command below, and when prompted, enter “Y” to confirm that you want to install it.
sudo apt install php-fpm php-mysql php-gd php-cli php-curl php-mbstring php-zip php-opcache
5. Configure Nginx to Execute PHP Files
Now that we’ve installed all of the LEMP components on our Debian 11 system, we need to edit the default Nginx virtual host configuration file.
sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/defaultCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Change the “location /” portion from this:
location / {
# First attempt to serve request as file, then
# as directory, then fall back to displaying a 404.
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}Code language: PHP (php)To this:
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}Code language: PHP (php)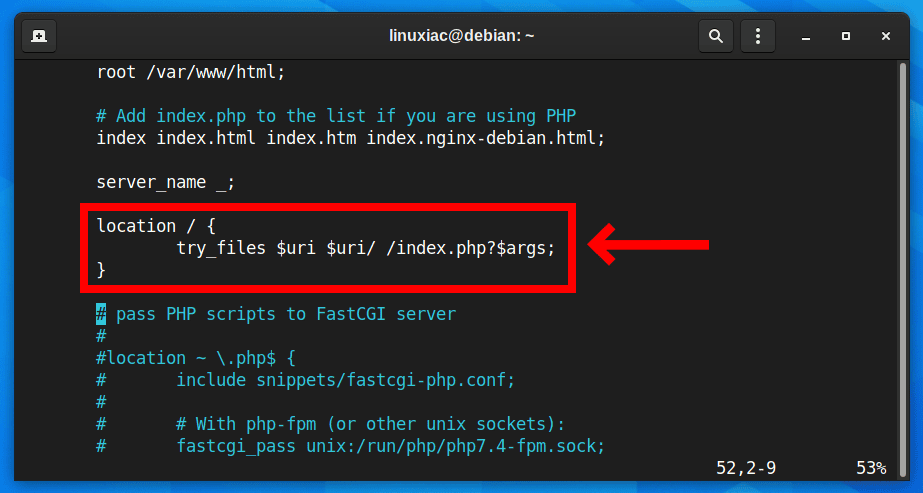
Add the following lines to the default “server” block to allow Nginx to process PHP files:
location ~ \.php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
}Code language: PHP (php)
Test the modified Nginx configuration file for syntax errors by entering the following command:
sudo nginx -t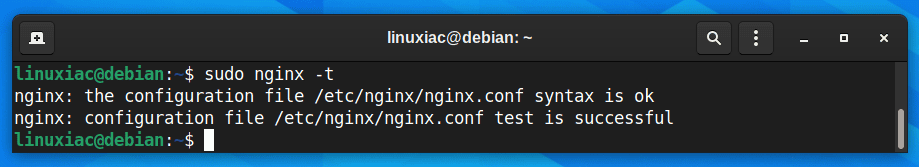
If you get the result shown above, all is well, and we only have one final step left. However, if any errors are reported, recheck your file before continuing.
When you are ready, restart Nginx to make the changes take effect.
sudo systemctl restart nginxIf you want to learn in detail how to create and edit Nginx server blocks for your virtual hosts, we recommend our excellent guide on the subject, “How to Create Nginx Virtual Host (Server Block).”
6. Test Your Debian 11 LEMP Installation
You have completed the installation of Nginx, MariaDB, and PHP on Debian 11, so your LEMP stack should now be fully operational.
Finally, let’s create a test PHP file to verify that PHP-FPM works and is integrated with Nginx. In the default server block above, our site is being served from “/var/www/html,” so we’ll create a test file there:
echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" | sudo tee /var/www/html/test.phpCode language: PHP (php)Now, you can access “test.php” from a web browser, using your site’s domain or server’s IP address followed by “/test.php.”
A web page with complete information about your PHP installation will appear.

Congratulations! You successfully installed a fully functional LEMP stack on Debian 11.
Conclusion
This guide showed you how to install the LEMP stack (Nginx, MariaDB, and PHP) on Debian 11 “Bullseye.” As a result, PHP-based web apps can now run on your server.
There are several next steps you could take from here. For example, I recommend that you read our guide on setting SSL certificates on the Nginx server to ensure that your website provides content over a secure SSL (HTTPS) connection.
Thanks for your time! I hope you find this guide useful. Your feedback and comments are most welcome.
