For Ubuntu users, the software can come from many sources. There are official repos, PPAs, Snap store, Flathub, etc. Sometimes, however, you won’t find every app you want in one of those. Instead, you may have to visit a website to download and install a file with a .deb extension.
But first, let’s answer the question, what exactly is a DEB file?
What is a DEB File?
The DEB files are an installable software package format used by Debian and its derivatives, such as Ubuntu, Linux Mint, etc. They contain precompiled software ready to be installed on Debian or a Debian-based operating system.
The DEB file is based on the archiving format, containing two TAR archives – installer control information and installable data. They contain all the necessary files and instructions for installing a specific software app. In addition, DEB files’ TAR archives are commonly compressed using bzip or gzip compression.
You can easily view DEB’s file contents by opening it as a standard archive file with your preferred archive/extract application.
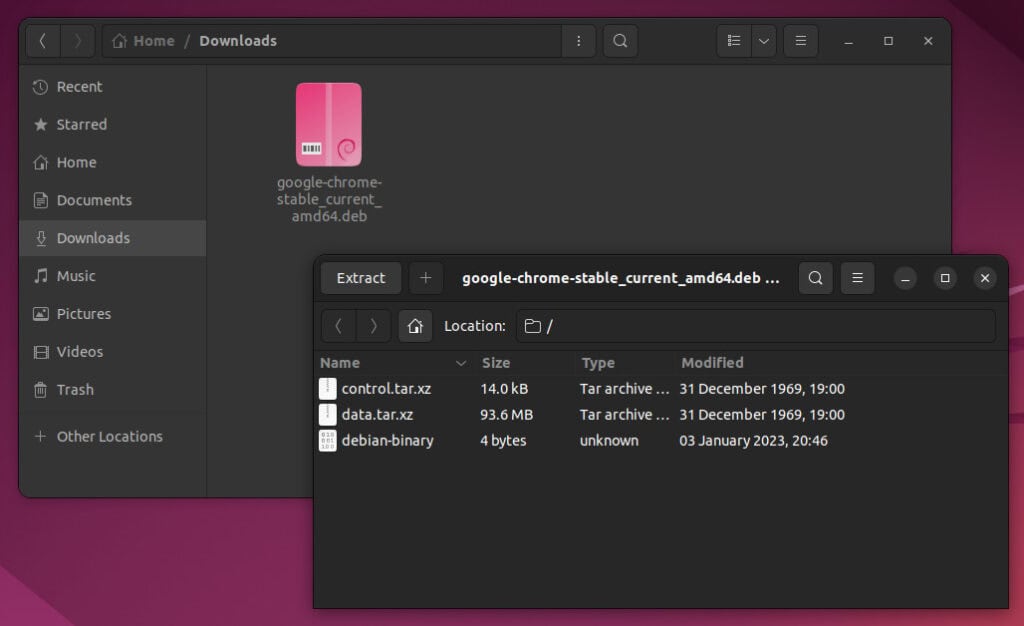
The following examples will use the Google Chrome installation DEB file “google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb.”
Install DEB File by Using apt Command
Before we get started, I’d like to clarify the following: many guides recommend installing a DEB file with the dpkg command. However, I do not recommend this approach; instead, please use the apt command. Here’s why.
When you use APT to install a package, dpkg is used under the hood. But APT first generates a list of all dependencies before downloading it from the repository. Then, when the download is complete, APT invokes dpkg to install all dependencies.
At the same time, there are no dependency checks when using the dpkg command directly. In other words, dpkg will not install package dependencies, often resulting in installation failures. Of course, you can fix this with some tricks, such as “sudo apt install --fix-broken,” which attempt to correct a system with broken dependencies in place, but that’s not the way I’d propose as a best practice.
Now, let’s get to work and show you how to install a DEB file in Ubuntu. The first approach is to use the APT command. It is a command-line utility for managing (installing, updating, removing) DEB packages on Debian and related Debian-based Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, Linux Mint, etc.
Additionally, if you want to learn more in-depth about the APT command and master your command-line skills, our thorough guide will come in handy.
APT is typically used to download and install software from remote repositories, but it can also be used to install DEB packages from local sources. So, let’s see how we can take a single DEB package and install it properly on Ubuntu. You must direct the apt command to the file’s location to perform the installation.
For example, to install the “google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb” file, open the terminal and type the following:
sudo apt install ./Downloads/google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb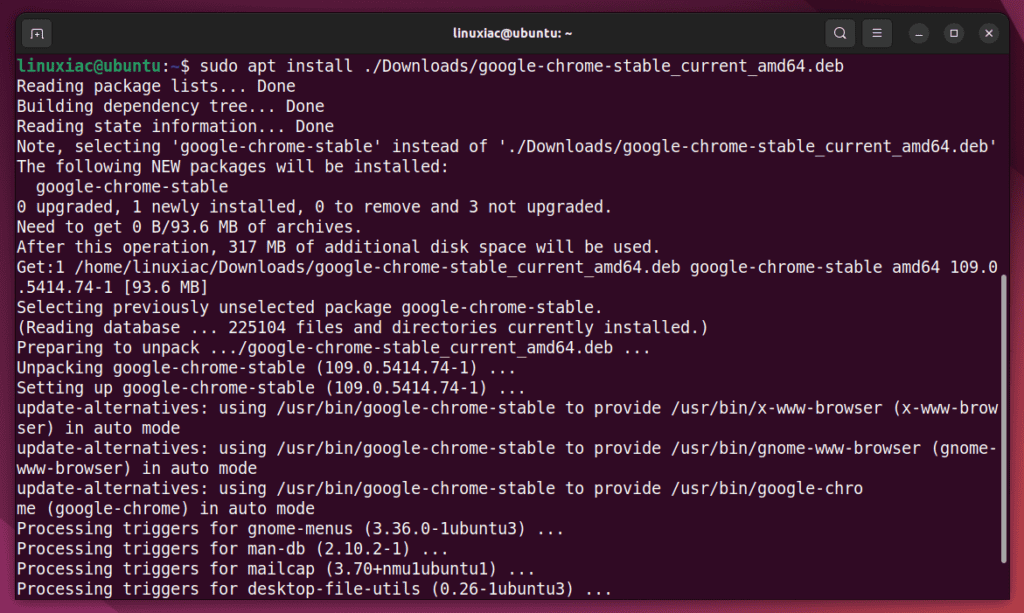
That’s all! Of course, you should replace “Downloads” with the path to the file on your Ubuntu system where it is stored and the name of the .deb file with the actual name of the file you’ve downloaded.
Install deb File by Using Ubuntu Software Manager
This is probably the easiest method for new Linux users to install .deb files in Ubuntu. It uses the built-in Ubuntu Software Manager.
Go to the folder where you downloaded the .deb file, right-click on it and choose the Open With Software Install option.
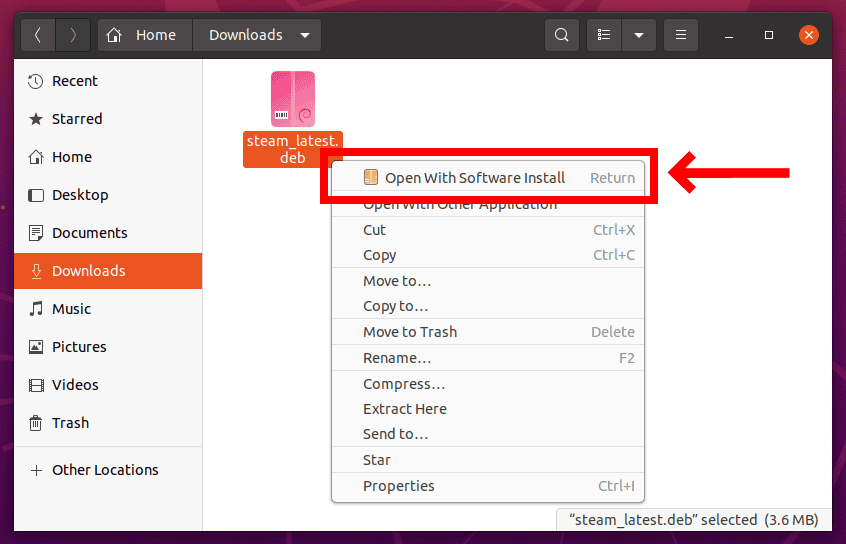
This will open the Ubuntu Software Manager. Then, all you have to do is to hit the Install button.
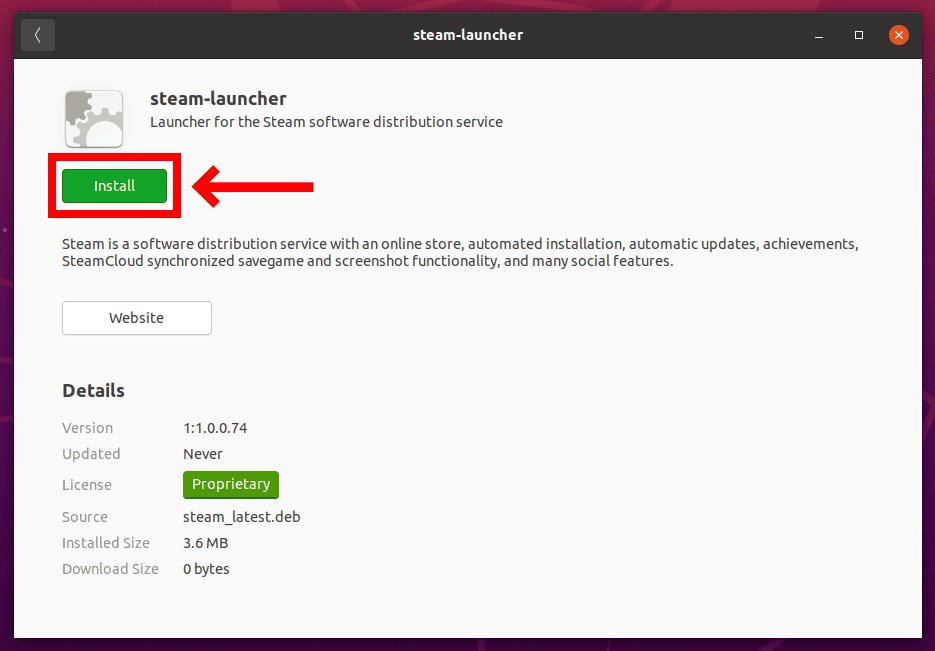
Enter your user password when prompted and hit Authenticate. As you know, only an authorized user can install the software in Ubuntu.
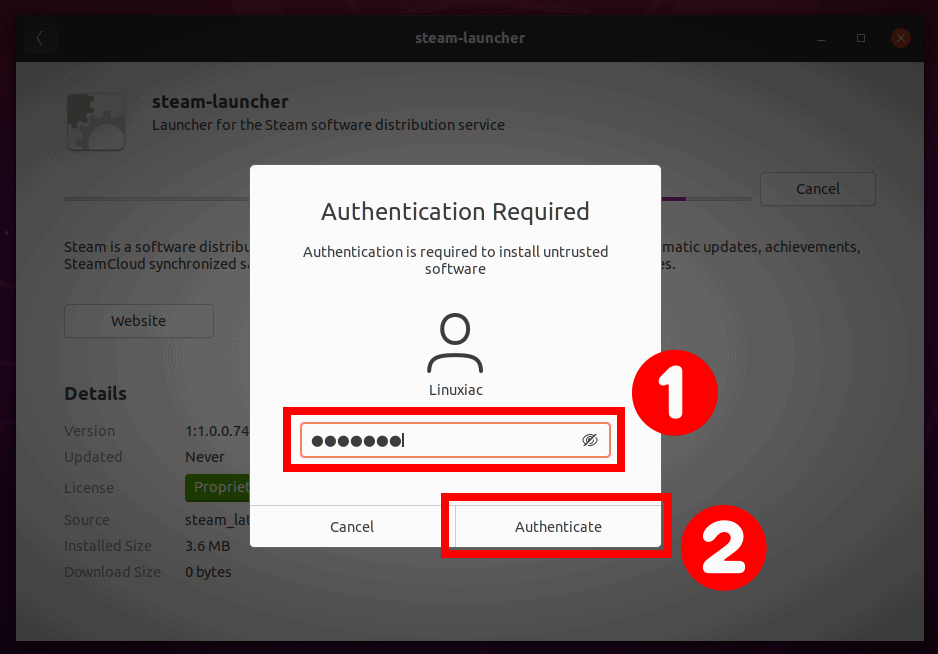
The progress bar lets you know when the app has finished installing on your Ubuntu system.
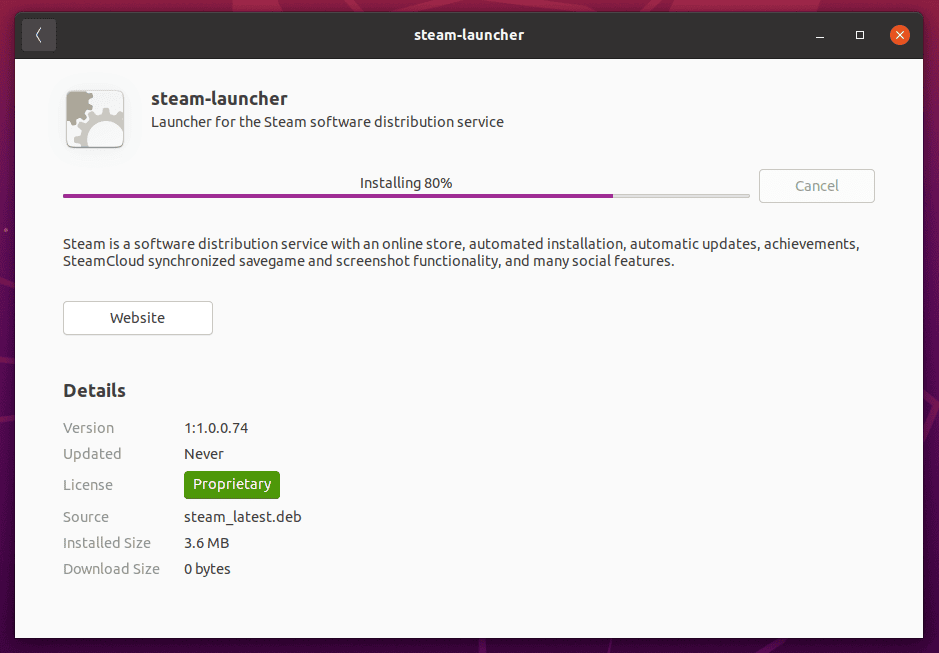
The software will be successfully installed on your system.
Conclusion
I hope this guide helps you to know various ways to install a .deb file in Ubuntu and other similar derivatives.
However, please keep in mind that you need to install .deb files on your Ubuntu system only if you’re confident about the file source and can verify its integrity.
Please find out more about various options in apt on its command line manual page.
As always, feel free to leave a comment if you have any questions.
