If you’re a Fedora user, you’re likely familiar with each new release’s frequent updates and improvements. Fedora, known for its cutting-edge features and commitment to Open Source principles, offers a seamless upgrade process to keep your system up-to-date with the latest software.
This article will guide you through upgrading from Fedora 37 to Fedora 38. So, whether you’re a seasoned Linux user or new to the Fedora ecosystem, this step-by-step tutorial will help you smoothly upgrade your system and take advantage of the exciting new features and enhancements that Fedora 38 offers.
We will show you two different approaches you can take – using the graphical interface of the Software application or the terminal if you prefer the command line way. So, without further ado, let’s get started.
Backing Up Your System
Before attempting a major upgrade on any system, you should ensure you won’t lose data if the upgrade goes wrong.
So before doing anything else, we strongly recommend a full system backup. Of course, you can always use a command like the one shown below, which will archive all of the more important directories and their contents in a tar.gz archive.
sudo tar czf /fedora37-backup.tar.gz \
--exclude=/fedora37-backup.tar.gz \
--exclude=/dev \
--exclude=/mnt \
--exclude=/proc \
--exclude=/sys \
--exclude=/tmp \
--exclude=/media \
--exclude=/lost+found \
/Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Add more “–exclude=” parameters if you need to. The command creates a backup of all files in “fedora37-backup.tar.gz” located under the root partition (/), which should be transferred to another computer or drive, for example, using the SCP command.
Upgrade to Fedora 38 from Fedora 37 Using GUI
Before you begin upgrading, ensure your system is fully up to date to guarantee a seamless upgrade. So, open the terminal and type:
sudo dnf updateIf any updates are available, install them and reboot the system if necessary. Once you’ve done that, you can move on to the next step.
In Fedora, upgrades are immediately available from the previous version whenever a new one is released.
Start the Software app by launching it from the GNOME dash, searching for “software,” and clicking to run the same when its icon appears.

Next, go to the “Updates” pane. You will see a notification that says, “Fedora Linux 38 Available”. Click the “Download” button to download Fedora 38 packages.
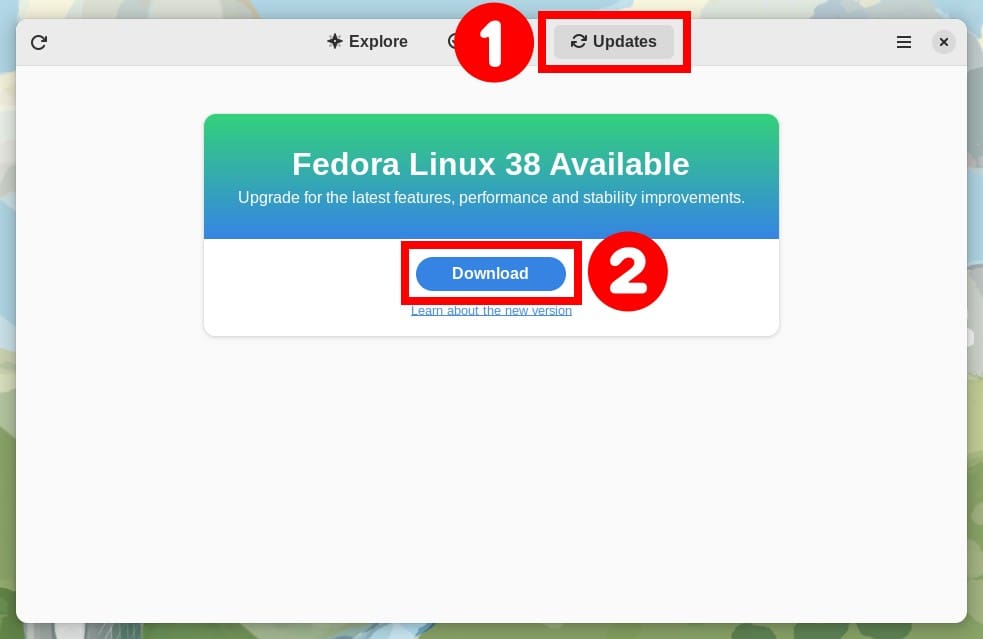
When you hit the “Download” button, all the packages required for the upgrade will be automatically downloaded. However, depending on your internet speed, the download will take some time, so be patient.
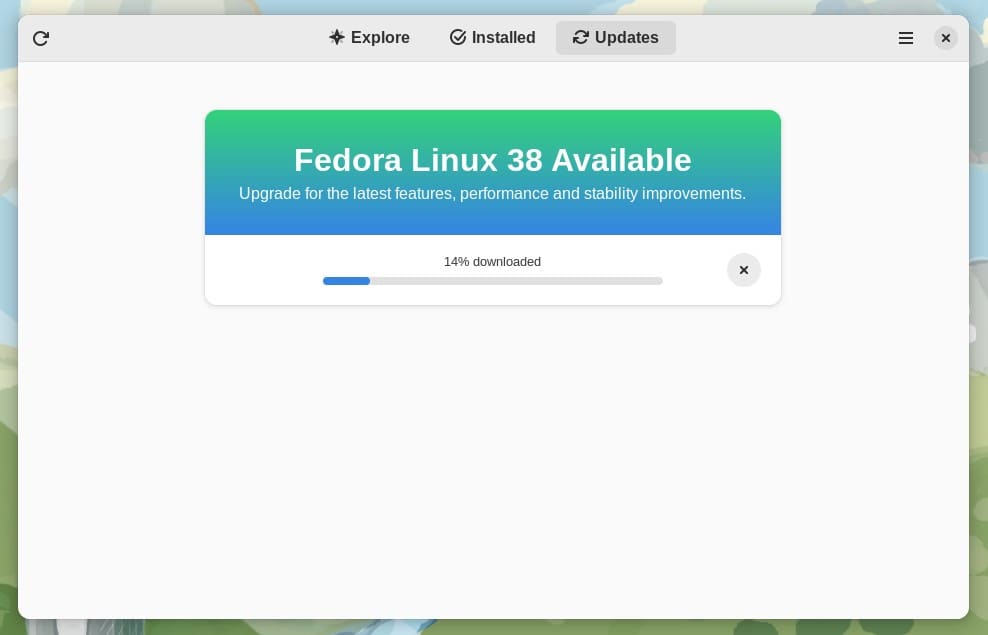
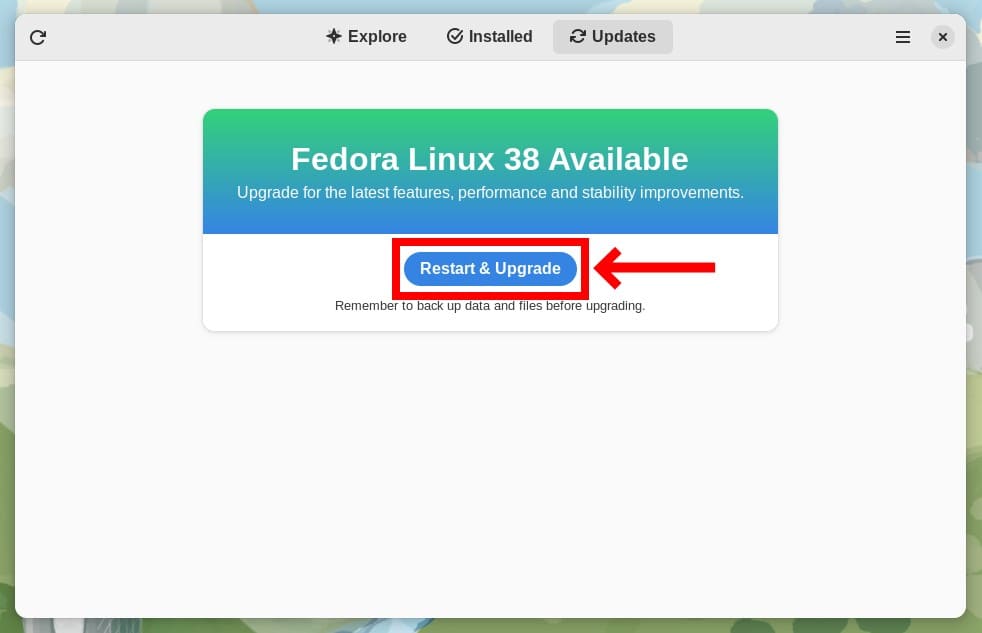
When the download is complete, click on the “Restart & Upgrade” button to start the upgrade process to Fedora 38.
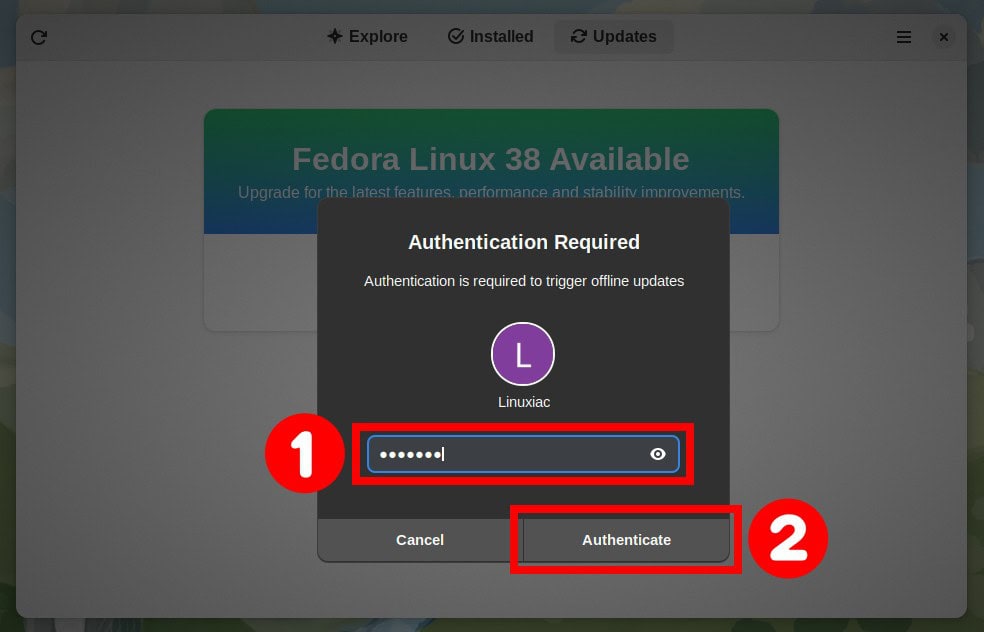
A popup window will appear and prompt you to enter the password for your user. So, enter it and confirm with the “Authenticate” button.
A new popup will ask you for confirmation to restart your system and begin the upgrade from Fedora 37 to Fedora 38. Next, click on the “Restart & Install” button.
As shown below, the system will restart to apply the downloaded system upgrades. The process will take some time, so please be patient and wait for the process to finish.
Once the upgrade completes, your system will boot into the newer Fedora 38.
Upgrade to Fedora 38 from Fedora 37 Using Command Line
1. Update Software
Ensuring you have the latest packages for all currently installed software is vital. To do so, enter the following command in a terminal:
sudo dnf upgrade --refresh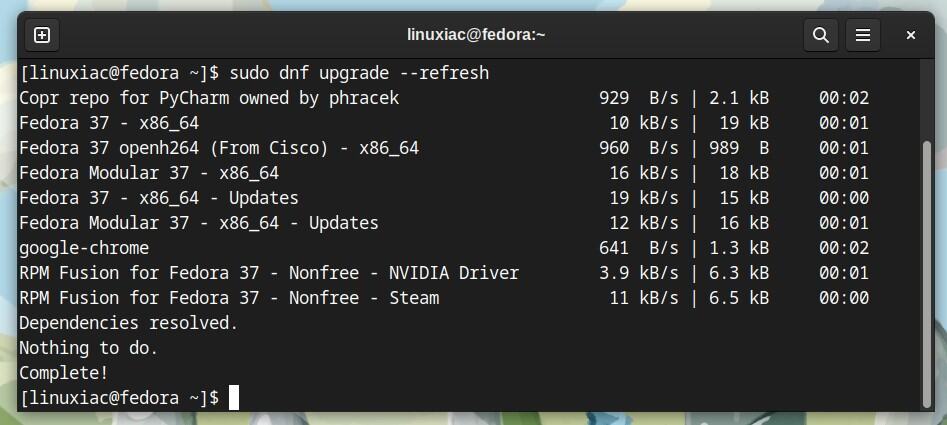
If you have any pending updates, install them and reboot the system if necessary.
2. Install the DNF Plugin
“dnf-plugin-system-upgrade” is a plugin for the DNF package manager and is used to upgrade your system to the current stable Fedora release.
Open a terminal and type the following command to install the plugin:
sudo dnf install dnf-plugin-system-upgrade3. Download the Updated Packages
Now start downloading the updates needed to move from Fedora 37 to Fedora 38 using the command:
sudo dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=38Next, you must manually approve the proposed system’s modifications in the following three steps by typing “Y” and then confirming by pressing “Enter.”
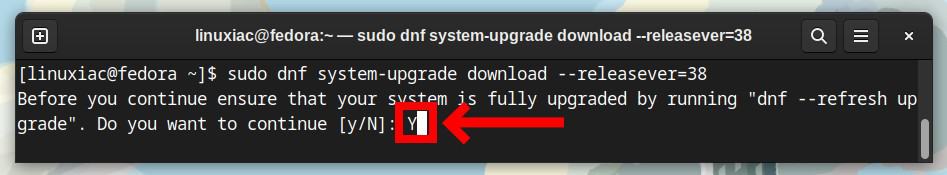
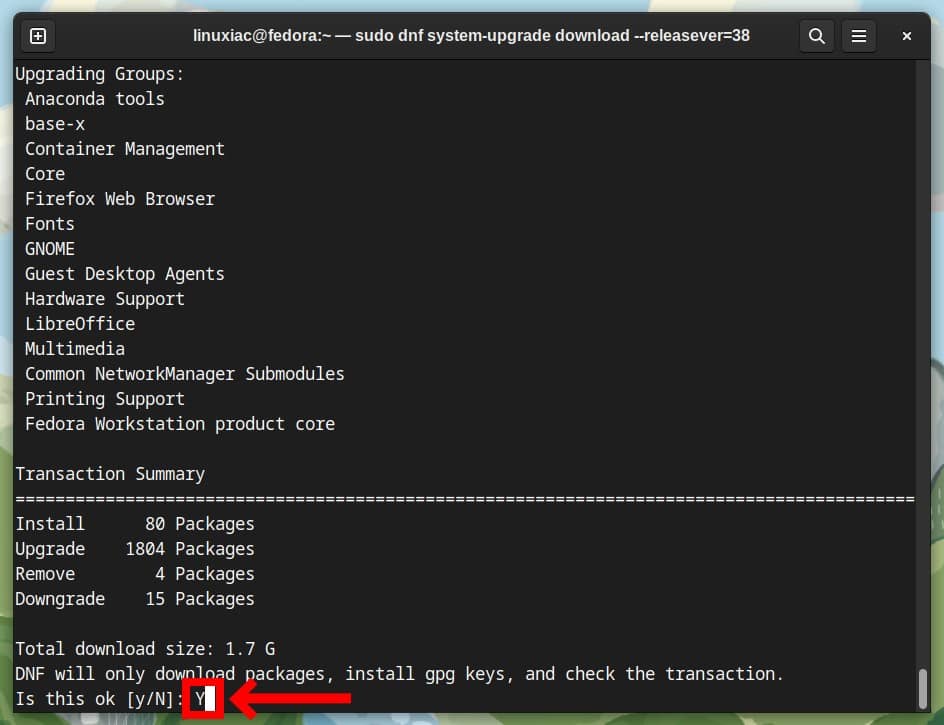
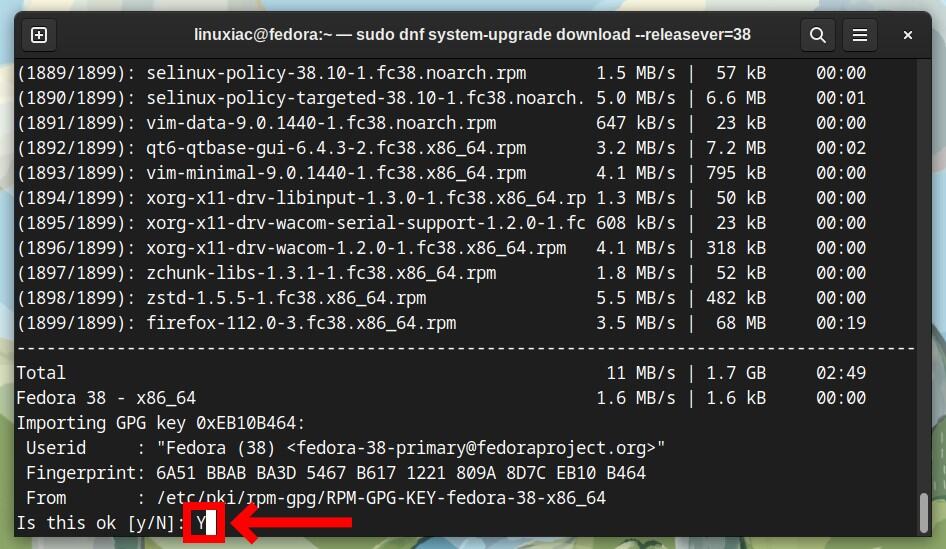
After downloading all the packages required to upgrade the system from Fedora 37 to Fedora 38, you will see the screen below.
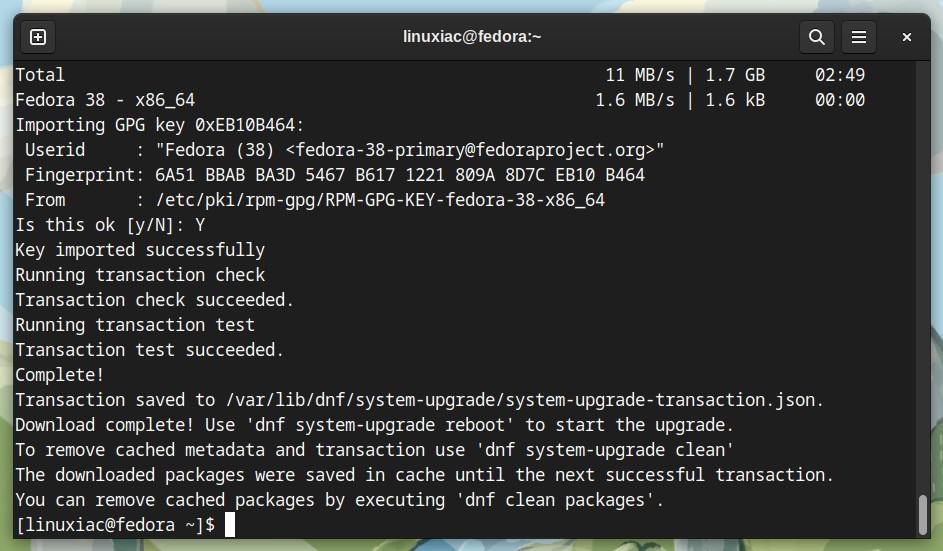
It should be noted that our current Fedora 37 system has not yet been upgraded. So, the actual upgrade will begin in the following step.
4. Start Fedora 37 to Fedora 38 Upgrade Process
Once you finish downloading the packages, run the following command to reboot your system and get into upgrade action:
sudo dnf system-upgrade rebootOnce the system reboots, it will automatically start the process. Upgrading the system will take some time, so you can relax and let it finish.
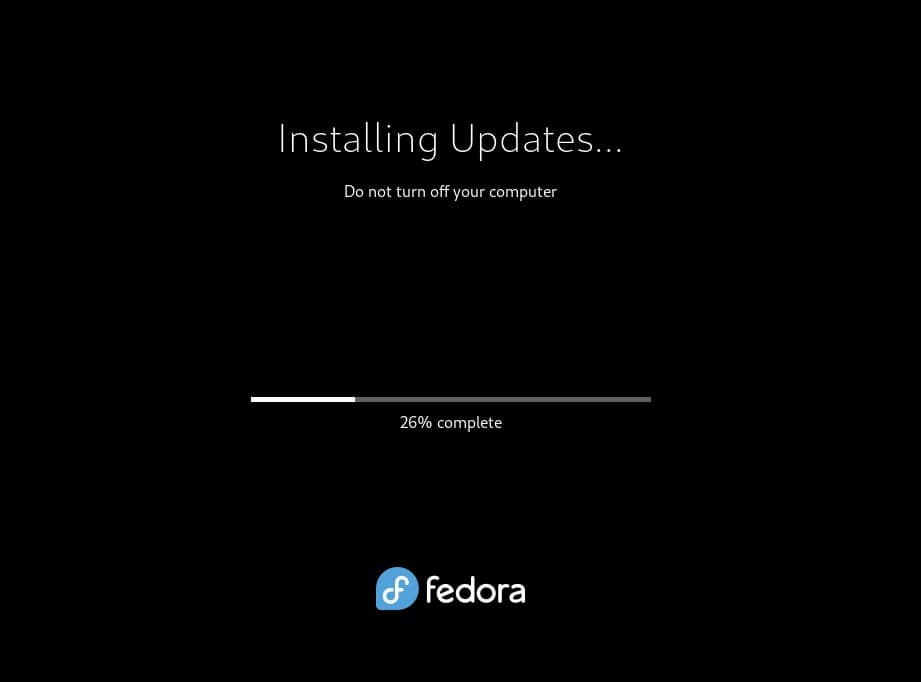
Once everything is complete, your system will reboot, and you can log in and enjoy your newly upgraded Fedora 38 system.
Conclusion
Upgrading to Fedora 38 from Fedora 37 is a straightforward process that can be accomplished with careful preparation and execution. Following the steps outlined in this article, users can ensure a smooth transition to the latest version of Fedora, which offers new features, improvements, and bug fixes.
Remember, it is crucial to back up all important data and configurations before upgrading to avoid data loss. After the upgrade is complete, it is recommended to thoroughly test the system to ensure that all applications and functionalities are working as expected.
For additional help or useful information, we recommend checking the official Fedora upgrade documentation.
