SQLite is an open-source self-contained, lightweight serverless relational database management system. It is a database, which is zero-configured, which means, like other databases, you do not need to configure it in your system.
Related: The 5 Best Free Replacements for MySQL Server
SQLite DB Browser is an open-source visual tool used to create, design, and edit database files compatible with SQLite. The software provides controls and wizards to handle various database functions in a comfortable visual medium. It runs on Windows, Linux, Mac, and FreeBSD.
SQLite DB Browser users will come across the most common database files with the file extension .db.
DB Browser for SQLite Features
DB Browser is for users and developers who want to create, search, and edit the SQLite databases. Its main features include:
- Create and compact database files.
- Create, define, modify and delete tables and indexes.
- Browse, edit, add and delete records.
- Search records.
- Import and export tables from/to CSV files.
- Import and export databases from/to SQL dump files.
- Issue SQL queries and inspect the results.
- Examine a log of all SQL commands issued by the application.
- Plot simple graphs based on a table or query data.
Install SQLite DB Browser on Linux
Ubuntu / Linux Mint
A PPA contains the latest release of SQLite DB Browser for Ubuntu or Linux Mint. To add this PPA to your system and install SQLite DB Browser from it, type in these commands in the terminal:
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:linuxgndu/sqlitebrowser
sudo apt update
sudo apt install sqlitebrowserDebian
Please run the following command to install it on Debian.
sudo apt install sqlitebrowserFedora
SQLite DB Browser is included by default in Fedora. To install it, just type:
sudo dnf install sqlitebrowserArch Linux
The package can be installed into Arch Linux using the Pacman package manager.
sudo pacman -S sqlitebrowseropenSUSE
openSUSE users can install it by typing in the following command in the terminal:
sudo zypper install sqlitebrowserHow to Use SQLite DB Browser
The initial screen of DB Browser will look something like this:
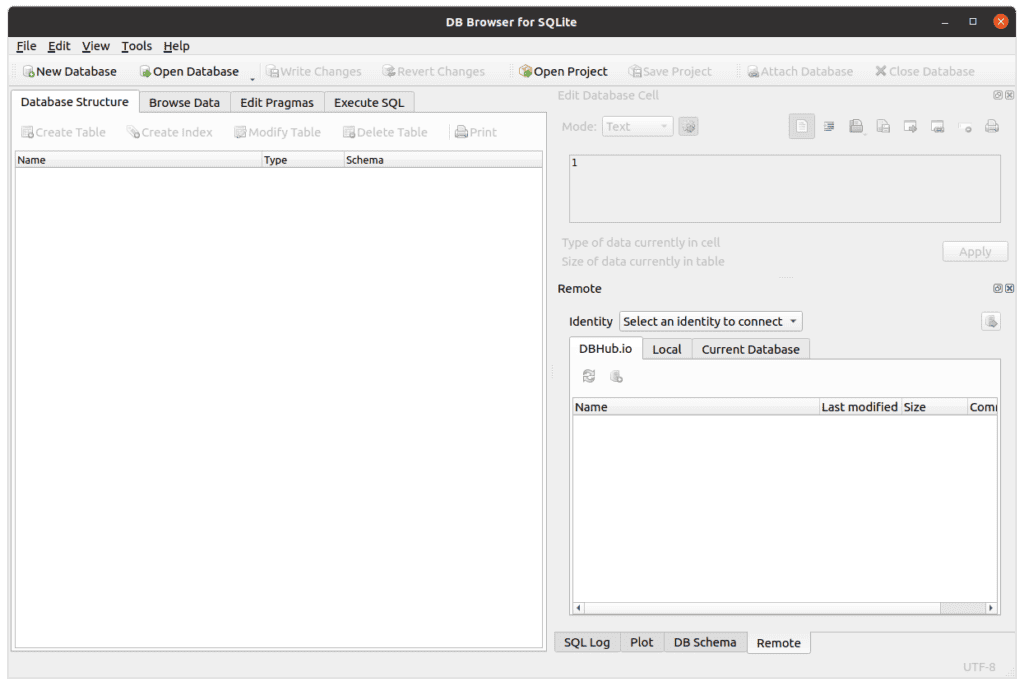
The four tabs on the upper left allow for easy database management.
- Database Structure: Create, list, and delete database tables.
- Browse Data: Browse values in tables, add rows and change values.
- Edit Pragmas: Control various environmental variables and state flags within the SQLite environment.
- Execute SQL: Use this tab to execute SQL commands.
Initially, these will be pretty empty as you haven’t created or opened a database yet.
Opening a Database
Opening a database file with SQLite DB Browser is, as you would expect, pretty straightforward.
To open a database file, do the following:
- Click on the “Open Database” button in the toolbar.
- Navigate to where you have stored the database file on your local machine.
- Select it and click “Open.”
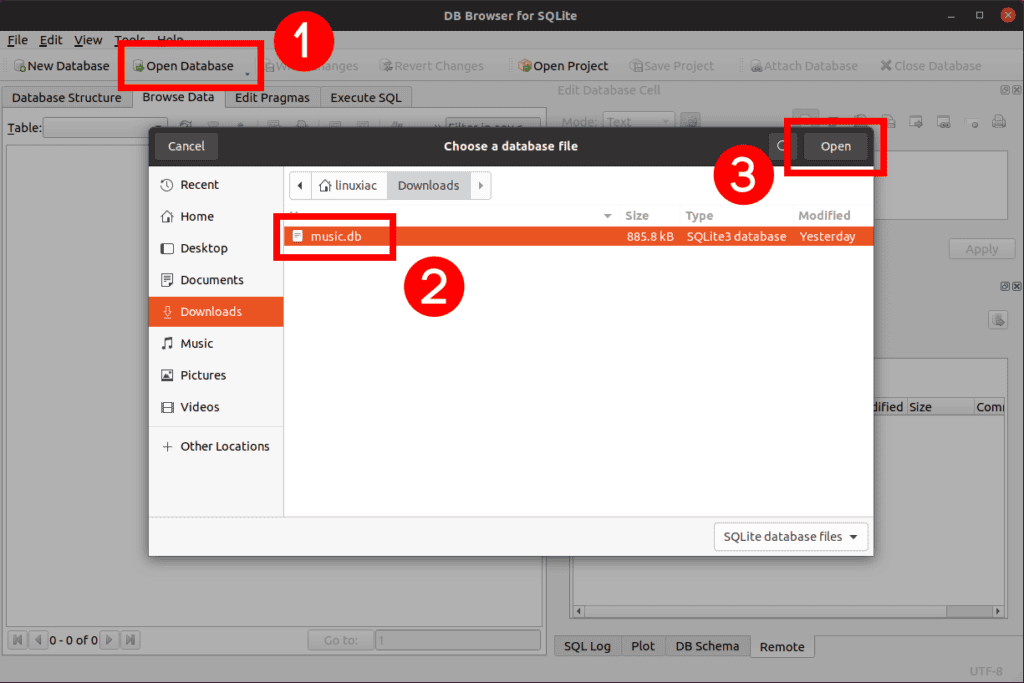
In addition, you can also drag a file directly into the user interface, and it will open the file.
If you do not already have a copy of this database, you can download the SQLite sample database from here.
Related: How to Create a Database in MySQL with MySQL Workbench
Browse the Data
You can browse your tables and view records by right-clicking on a table name and choosing the “Browse Table” option.
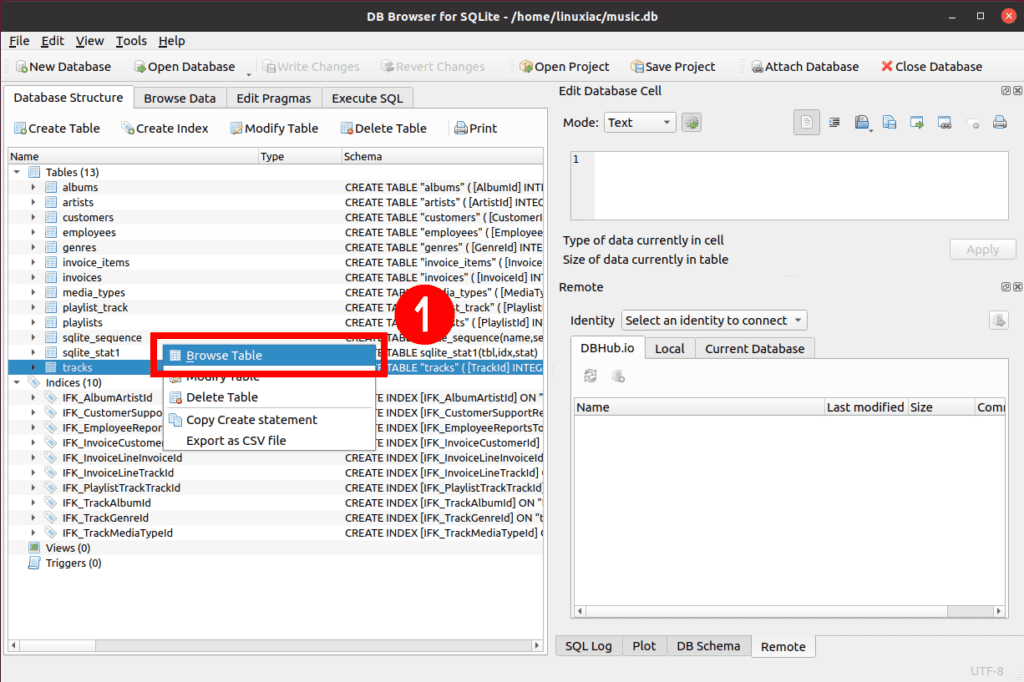
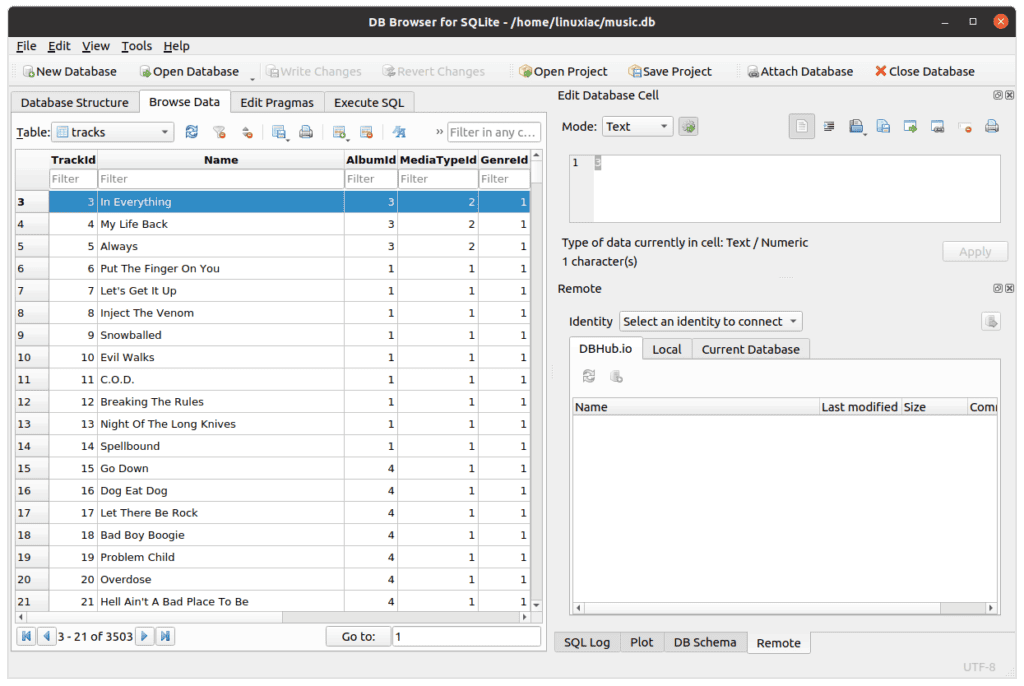
As a result, the table records are displayed.
Running SQL Queries in SQLite DB Browser
Of course, the power of a database resides in its ability to find and extract records. We use the SQL language with an SQL-compatible database to do this.
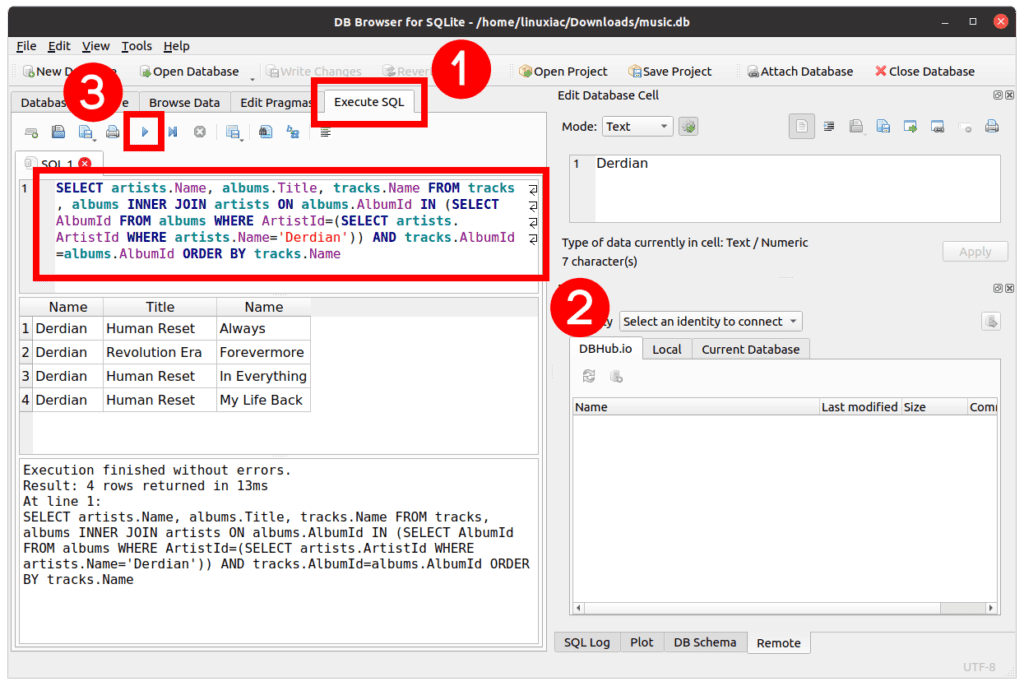
DB Browser supports writing SQL queries directly under the “Execute SQL” tab. So let’s run a query to see how it works.
Type the query and click the blue arrow to execute your SQL command. The results are displayed in the lower pane.
Conclusion
SQLite DB Browser is a powerful tool for interacting with SQLite databases. It was made to be used by both developers and end-users.
SQLite DB Browser was not made to be a shell for SQLite, nor does it require knowing SQL. Instead, it’s simply a visual tool to help users work with SQLite databases
For more information about it, you can visit the project’s website.
