- What Is Pacman Package Manager?
- What Will You Learn in This Guide?
- Refresh Package Lists
- Searching for Package
- Getting Information About Package
- Installing a New Package with Pacman
- Installing a Local Package
- Update/Upgrade a Package
- Remove a Package with Pacman
- Remove Orphaned (Unused) Packages
- Searching for Already Installed Packages
- Find All Files Owned by a Package
- Find the Package Owner of the File
- Download a Package
- Clean-Up Package Cache
- Conclusion
Want to install packages on Arch Linux but need to know how? Many people run into this issue when they first move to Arch. But don’t worry; you can easily manage packages on your Arch system using the pacman command. But first, let’s answer an important question.
What Is Pacman Package Manager?
Pacman (stands for Package Manager) is the default package manager for Arch Linux, a lightweight and flexible distro popular among experienced Linux users. Like Arch, Pacman is known for its simplicity, speed, and reliability, combining a simple binary package format with an easy-to-use build system.
Pacman keeps the system up to date by synchronizing package lists with the official Arch repositories. In addition, this client-server model allows the user to download/install packages with a simple command, complete with all required dependencies.
What Will You Learn in This Guide?
We will cover the basics of Pacman, including how to install, update, and remove packages, as well as some more advanced features and tips for using Pacman to its full potential. So, whether you are new to Arch or an experienced Linux user, this guide will help you get the most out of the Pacman.
In addition, this guide also applies to all Arch-based Linux distros, such as Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Garuda Linux, etc., using Pacman as the package manager.
Of course, the official packages are just one of the sources of software on Arch. In addition, you can install some of the thousands available in the AUR repository – Arch’s most significant asset that differentiates it from all other Linux distributions.
However, to do this, different Pacman tools are used, known as AUR helpers. In that case, our comprehensive guide on the subject, “How to Install AUR Packages in Arch Linux,” will greatly help you.
Finally, you can even use one of the excellent GUI Pacman frontends to make installing packages in Arch as easy as possible.
Refresh Package Lists
Because Arch is a rolling-release distro, new packages are added to the distro’s repositories as soon as they are released. As a result, you should keep the Pacman database up to date by updating it fairly frequently.
So, to update the package lists before installing any packages or updating the system, perform the following:
sudo pacman -Sy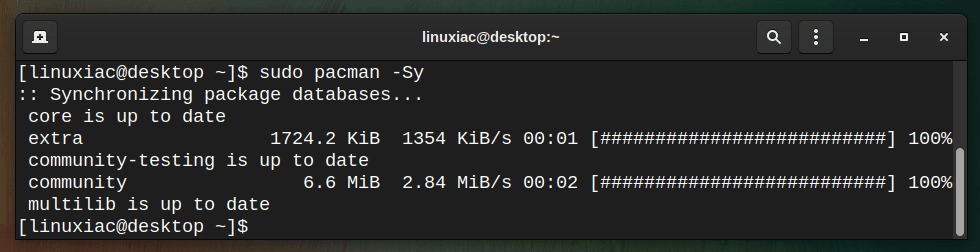
Searching for Package
To search for a specific package, for example, vlc, from a sync database (remote server), run:
sudo pacman -Ss vlc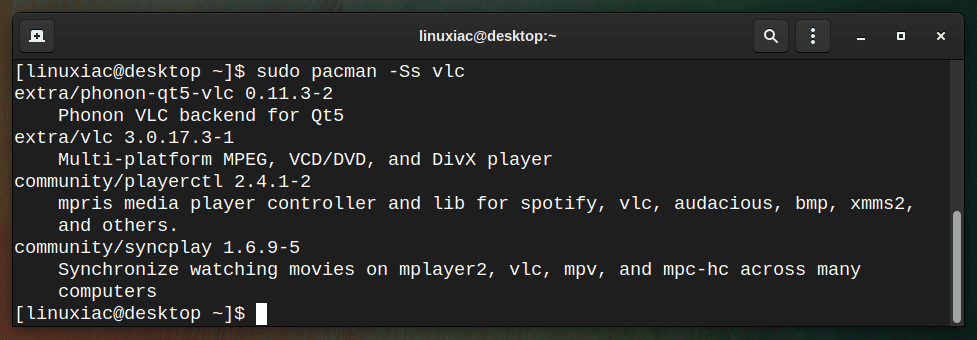
This returns all packages with a matching “vlc” string in the package name or description.
Getting Information About Package
To display the detailed information of the given package from the sync database, for example, nginx, run:
pacman -Si nginx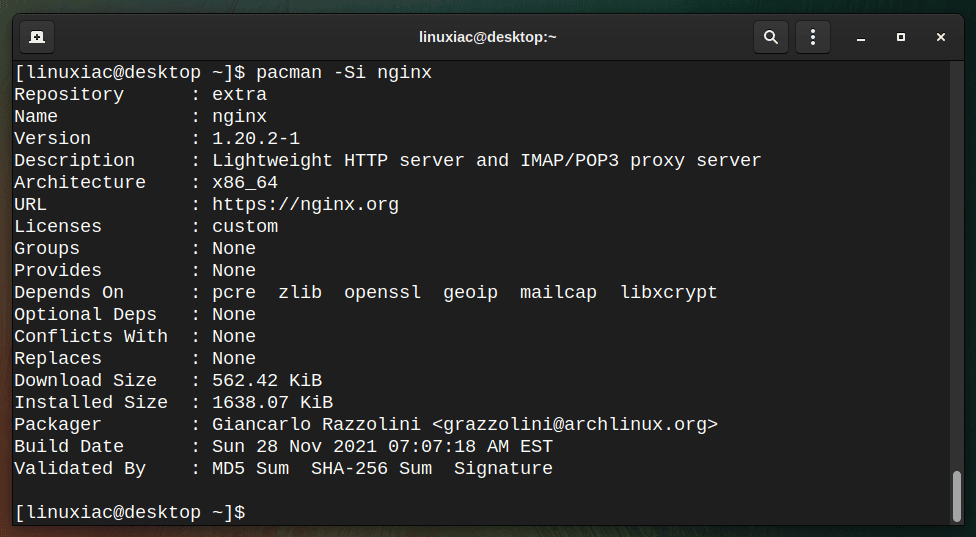
Installing a New Package with Pacman
Installing a package with Pacman is easy. Just run the following command:
sudo pacman -S vlc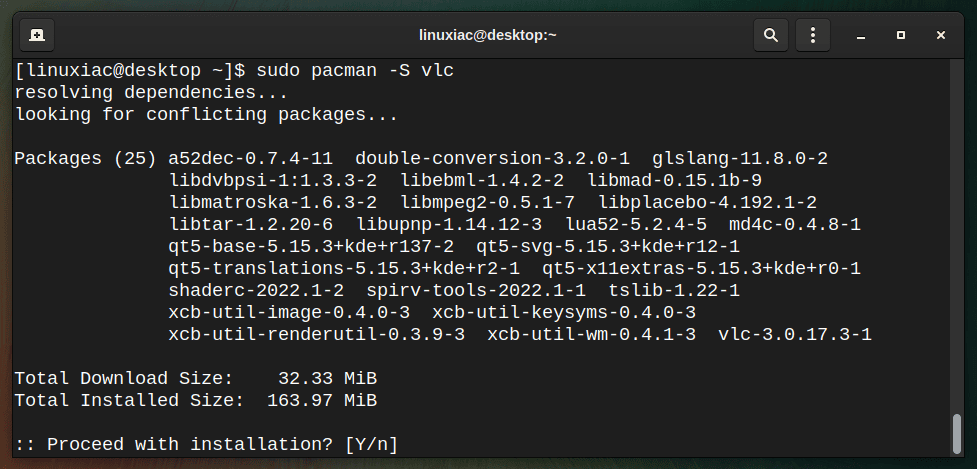
As a result, this process will automatically identify all the necessary dependencies and take care of them. In addition, to install multiple packages with a single command, use a space-separated list of packages.
Installing a Local Package
Pacman stores all downloaded packages in the /var/cache/pacman/pkg directory.
In case you want to install the locally downloaded package, for example, vlc, located in /var/cache/pacman/pkg/ directory, go to the folder where the package is located and enter the following command:
cd /var/cache/pacman/pkg/
sudo pacman -U vlc-3.0.11-2-x86_64.pkg.tar.zstCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Update/Upgrade a Package
To update a single package, for example, rsync, run the following:
sudo pacman -S rsync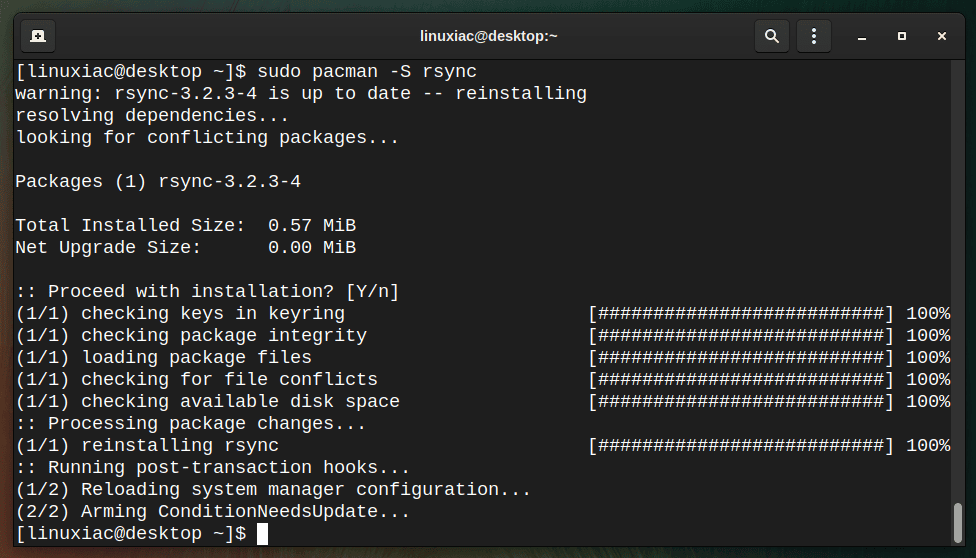
To update all packages at once on your system, just run the following:
sudo pacman -Syu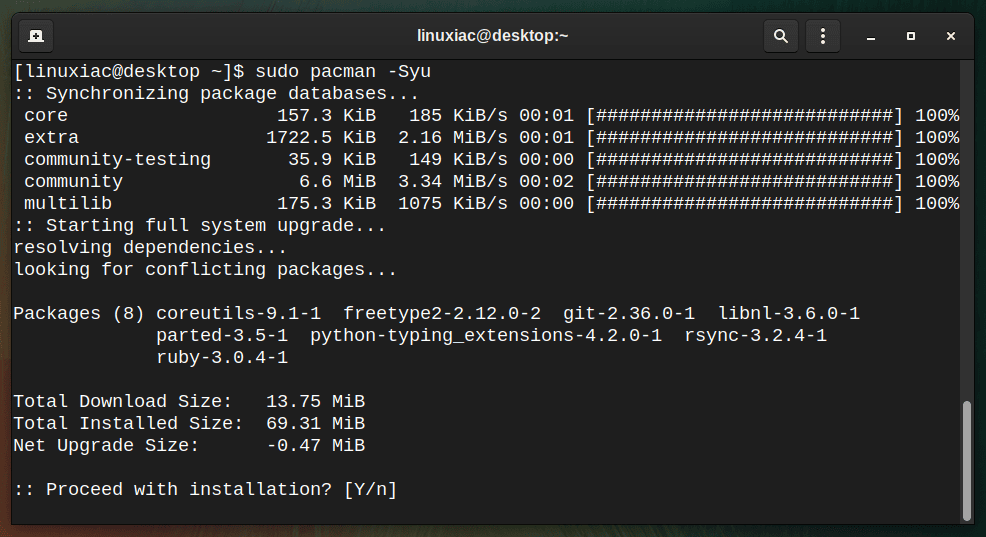
However, sometimes you want to upgrade the packages, but you want it to stay at an older version (because you know the newer version has removed a feature or is broken).
So, if the vlc package was causing the problem, you could use the following command for this:
sudo pacman -Syu --ignore=vlcRemove a Package with Pacman
To remove a package alongside with all its dependencies, run the following command:
sudo pacman -Rs vlc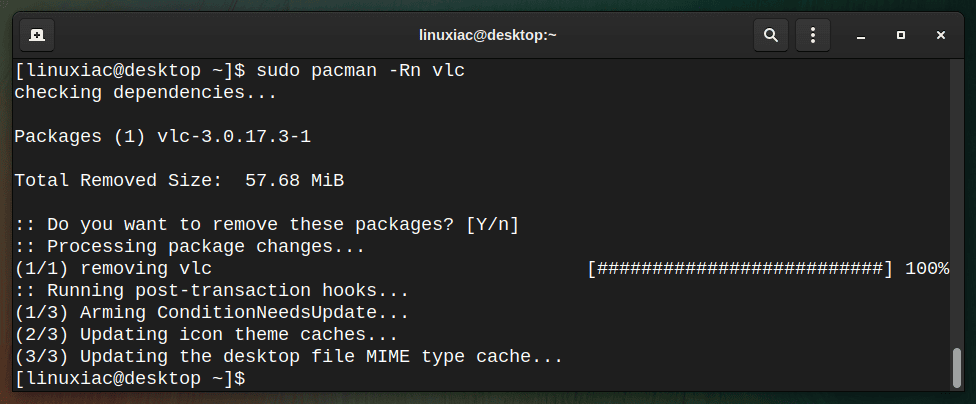
This command will altogether remove the vlc package and all dependencies. While removing packages, Pacman will keep the critical configuration files with the extension .pacsave.
In addition, if you no longer want them and want to free up the hard drive, you can remove the package along with all its configuration files with the command:
sudo pacman -Rns vlc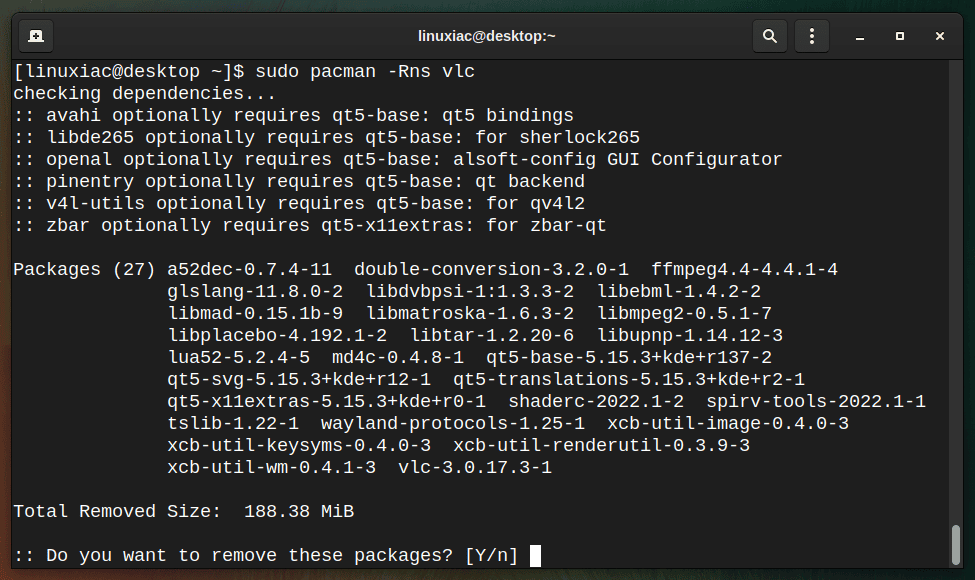
Remove Orphaned (Unused) Packages
After removing a package in Arch Linux, there may still be some remaining orphaned (unused) packages that were dependencies of the removed package. However, these orphaned packages are not required anymore, so we can get rid of them to free up some space.
To remove these packages, run:
sudo pacman -Rns $(pacman -Qdtq)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)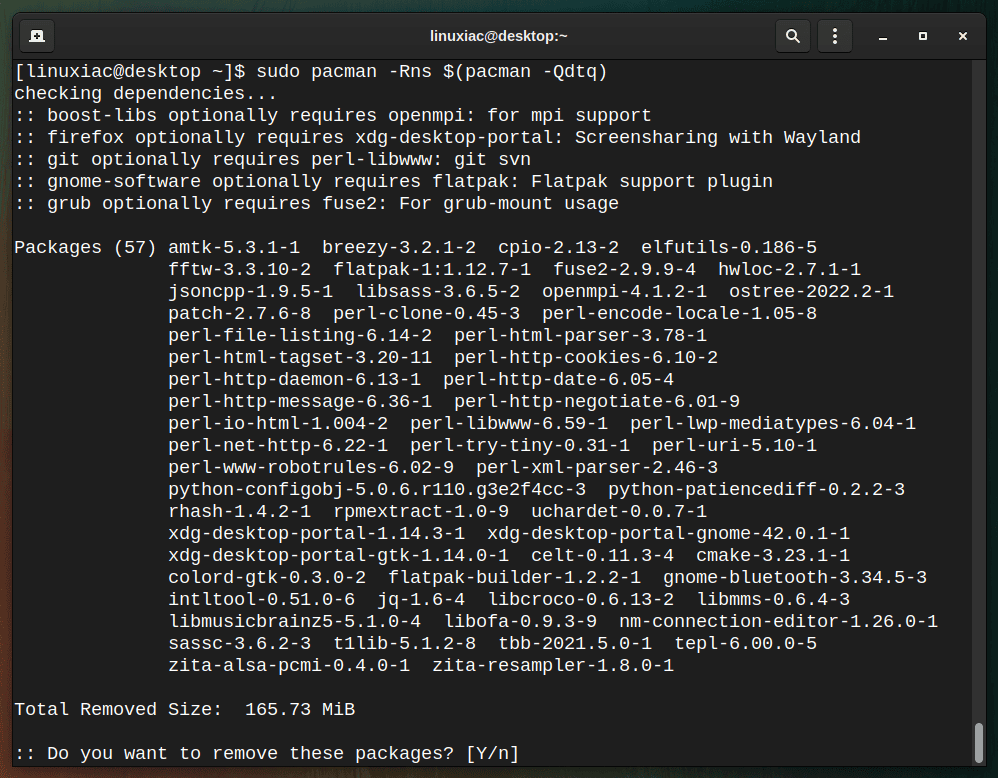
If no orphans were found, the output is:
Searching for Already Installed Packages
Sometimes you want to check for a specific package if it is installed locally. In this case, you can do it using the command below:
pacman -Qs vlc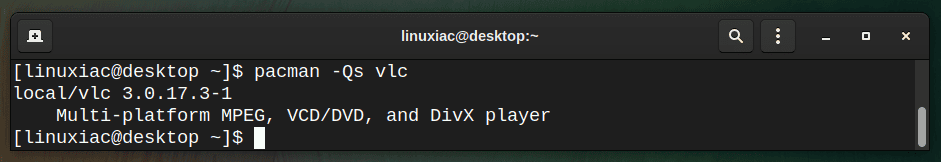
You can view a list of all the packages installed on your system using the following command:
pacman -QFind All Files Owned by a Package
You can find all the files that are installed by a specific package using the following command:
pacman -Ql vlc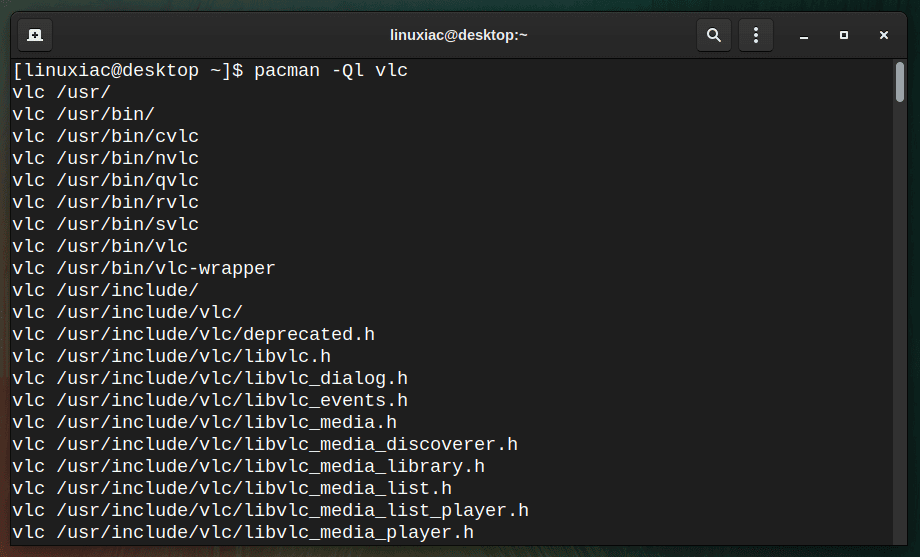
This returns the package name and the path to files that it owns.
Find the Package Owner of the File
If you want to check the location of the binary executable file owned by a package, use the -Qo flag.
pacman -Qo /usr/bin/vlc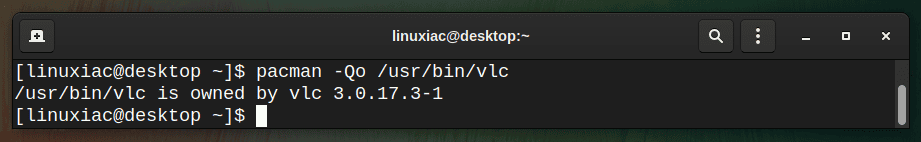
Download a Package
Sometimes, you can download a package and keep it in your cache without installing it. For example, you can use the downloaded package later. To do so, run:
pacman -Sw vlc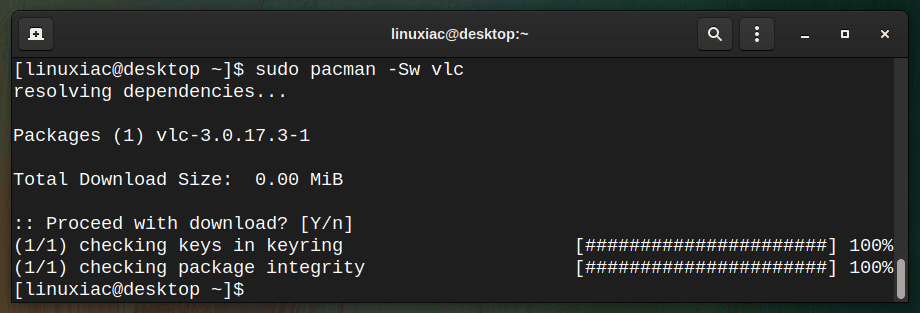
The above command will only download the vlc package and keep it in the cache folder. Pacman stores all downloaded packages in the /var/cache/pacman/pkg directory.
Clean-Up Package Cache
All packages we downloaded during the installation will be stored in the cache directory, i.e., /var/cache/pacman/pkg/. But if you don’t remove them periodically, they will slowly eat up your hard drive space; sooner or later, you could end up with low disk space.
So it is good to remove the cache periodically. For example, to remove all the cached packages and the unused sync database, execute the following:
sudo pacman -Sc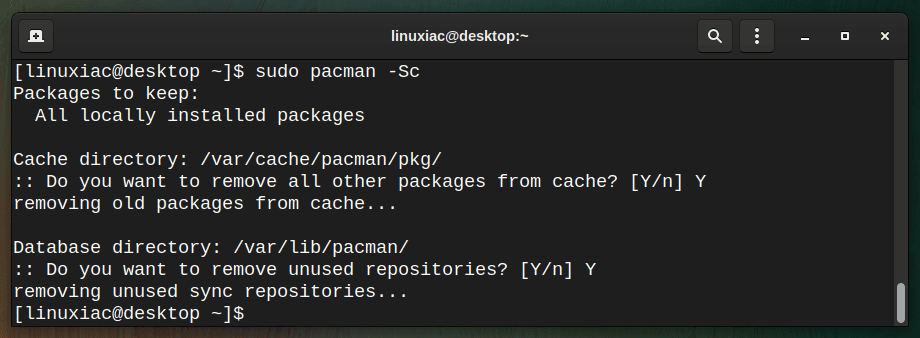
In addition, if you want to remove all files from the cache, use the clean c switch twice. Of course, this is the most aggressive approach and will leave nothing in the cache folder:
sudo pacman -Scc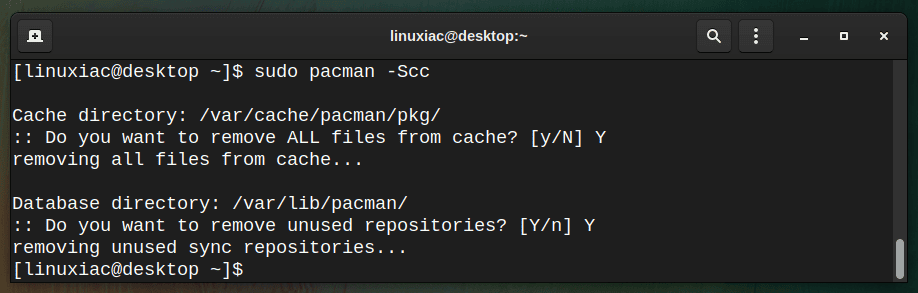
Conclusion
Arch Linux is one of the most reputed and famous Linux distributions. This guide has covered most of the commands you need to know when using Pacman to install, update, and remove software on Arch.
We also strongly suggest checking out our guide, “Finding the Most Up-to-Date and Fastest Arch Linux Mirrors.” It will enhance your experience with Pacman and increase your knowledge.
I hope that it was helpful in your journey with Arch. For more information, refer to the Arch Linux Wiki, which provides official documentation about the Pacman package manager.

Pacman is broke and I can’t find a solution. Can you offer any suggestions or things I can read? I’ve been reading through the arch wiki and forums and haven’t found anything yet. Thanks for any advice and directions.
What happened:
I did sudo pacman -Syu and it appeared to upgrade successfully.
But now when I use pacman I always get: Error while loading shared libraries: /usr/lib/libgpgme.so.11 file too short.
I can’t install pacman-static from the AUR because when I try to makepkg it, it wants to use pacman, which gives the above error.
I used the ISO install disc but after I mount all my partitions and try sudo pacman -S gpgme, it tries to work but at the end it errors.
After I arch-chroot into /mnt, using pacman again gives the above error.
I use LXQt and all of my programs won’t show the header bar so I can’t resize them. I also lost three of my desktop switchers. It won’t detect my usb thumb drives now. My PCman file browser window is now 1/2 the size of the screen.
Hi Keith,
Try the things described here:
https://bbs.archlinux.org/viewtopic.php?id=285100
Best,
Bobby
Hi Bobby,
Just a courtesy follow-up.
I didn’t reinstall Arch. I figured that was an easy, non-academic way of resolving my computer issues. So I kept searching and digging, and I corrected all of my issues. And I can use pacman now.
I reconfigured Openbox, and also reinstalled LXQt. I had a Fontconfig error which led me to find some empty files in Googles Noto TTF fonts. There were also some empty libgpg* files that I had to reinstall. I also reinstalled archlinux-keyring.
Luckily there are enough posts in the Arch forums and I found posts where people had similar issues to mine so troubleshooting was interesting. Along with great error messages and debugging.
Regards,
Keith
Hey Keith,
Admirations on doing it the Arch way – one of the best approaches to learning Linux!
Best,
Bobby
Hi, Thanks for the quick response! Unfortunately I did not have any luck trying all those things on that page. I guess tomorrow I’ll spend some time and do a full install. Haha I kinda figured this would happen so I’ve already made notes and made some backup copies of files. Thanks again, Happy Holidays.
Thank you for posting this guide. I have saved your efforts as a .pdf. Much appreciated from Ca.
Great! Glad it was helpful. 🙂