Firefox is one of the most popular web browsers in the world, known for its functionality, security, and reliability. While the default version of Firefox on Debian 11 is the Extended Support Release (ESR) version, some users prefer to use the latest stable release of Firefox for its new features and improvements.
This blog post will guide you through installing the latest (non-ESR) version of Firefox on Debian 11, so you can enjoy the latest features and enhancements in your web browsing experience. But before we go any further, let’s explain something important.
What’s the Difference between Firefox and Firefox ESR?
Firefox and Firefox ESR (Extended Support Release) are web browsers developed by Mozilla, but they have some key differences.
1. Release Cycle
Firefox has a rapid release cycle, which means that new versions of the browser are released every four weeks, with regular updates and security patches. On the other hand, Firefox ESR has a slower release cycle, with new versions released every year or so, with only critical security updates released in between.
2. Stability
Firefox ESR is designed for organizations and enterprises prioritizing stability and compatibility over new features. So, because Firefox ESR is more stable, some Linux distro developers prefer it, which is precisely the case with Debian – a distro well-known for its conservative and careful approach to included software, prioritizing security and stability first.
On the other hand, Firefox targets regular users who want the latest features and improvements as soon as they are released, even if they may be less stable or require more frequent updates.
Now that we’ve cleared that up let’s get to the meat of the matter: how to install the most recent stable non-ESR version of Firefox on Debian 11.
Method 1: Install Firefox on Debian 11 from Ubuntuzilla Repository
This is preferred because it uses the native Firefox DEB installation package. Additionally, this approach guarantees you always get the latest up-to-date version and will automatically receive all future software updates as they become available. So, let’s get started.
Here is the default Firefox ESR running on our Debian 11 system.

Step 1: Remove Firefox ESR
The first step is to uninstall the current version of Firefox ESR on our Debian 11 system. If you do not do this and try to install the regular Firefox version with the existing Firefox ESR, an error message will appear, and the installation will fail. So, let’s do it.
sudo apt purge firefox-esr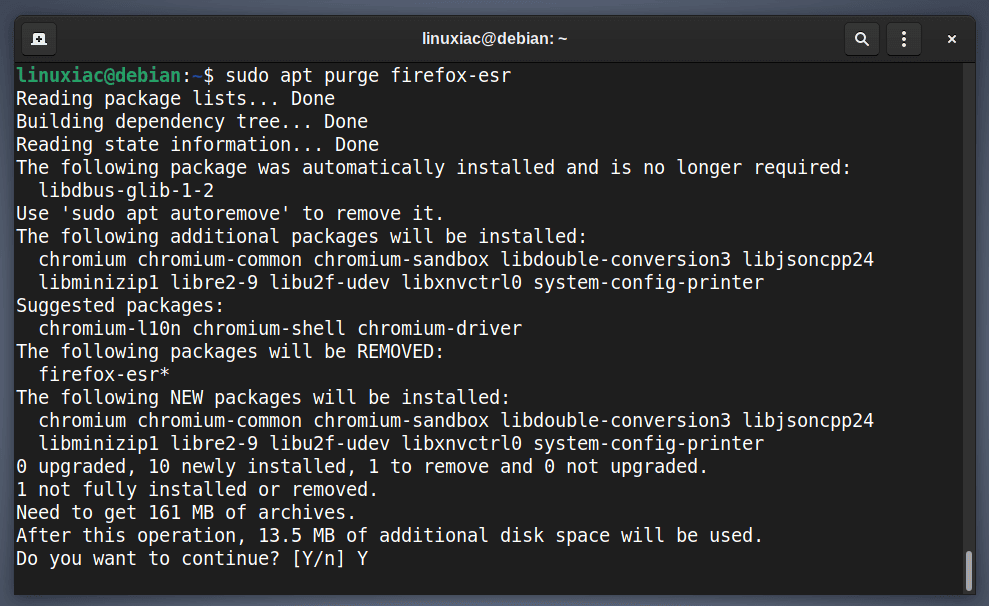
When we uninstall Firefox ESR from our Debian 11 system, we can proceed to the next step, adding the Ubuntuzilla repository.
If this is the only browser on your system and you are concerned, you can always install another. For example, here’s our easy-to-follow guide on how to install Google Chrome on Debian 11.
Step 2: Add the Ubuntuzilla Repository GPG Key
Ubuntuzilla project hosts an APT repository with DEB packages of the latest official release versions of Firefox, SeaMonkey, and Thunderbird – this repository work on any APT-based distribution, including Ubuntu and Debian.
Therefore, it is the perfect candidate for installing the most recent stable version of Firefox on our Debian 11 system and receiving regular updates when a new browser version is released.
Create the directory that will store the GPG keys used to sign the repository packages.
sudo mkdir /etc/apt/keyrings/If the directory exists already, you will be informed that it cannot be created, which is perfectly normal.
Next, import the Ubuntuzilla GPG repository key to your Debian system. This security feature ensures that the software you’re installing is authentic. Then, run the three commands listed below in the order provided.
sudo gpg --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys 2667CA5C
sudo gpg -ao ~/ubuntuzilla.gpg --export 2667CA5C
cat ubuntuzilla.gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/ubuntuzilla.gpg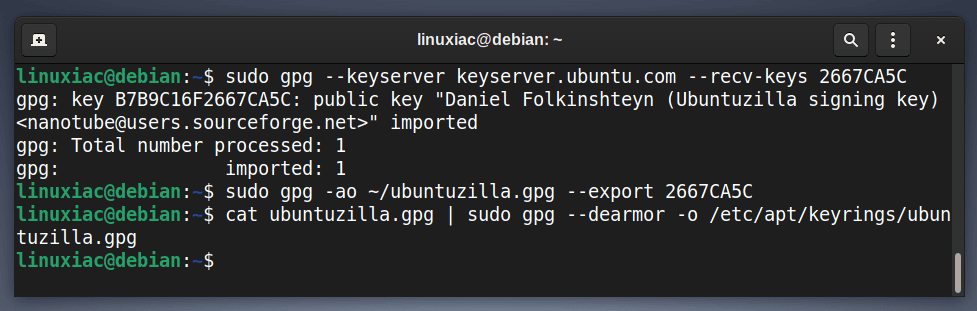
You can now safely delete “ubuntuzilla.gpg” from your home directory because it is no longer required.
sudo rm ~/ubuntuzilla.gpgStep 3: Add the Ubuntuzilla Repository to Debian 11
After importing the GPG keys, we’ll add the Ubuntuzilla repository to our Debian 11 system. This implies that the update package will be made available with the rest of your system’s regular updates if a new version is released.
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/ubuntuzilla.gpg] http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/ubuntuzilla/mozilla/apt all main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ubuntuzilla.list > /dev/nullCode language: PHP (php)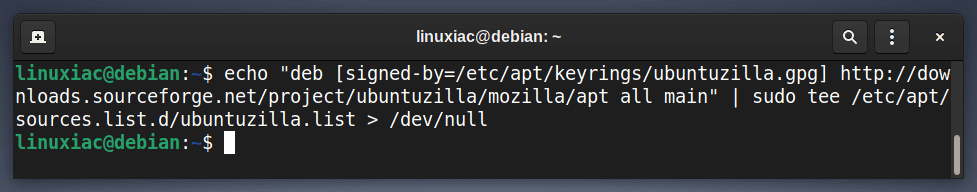
Notice that the command produces no output.
Next, refresh the package list.
sudo apt update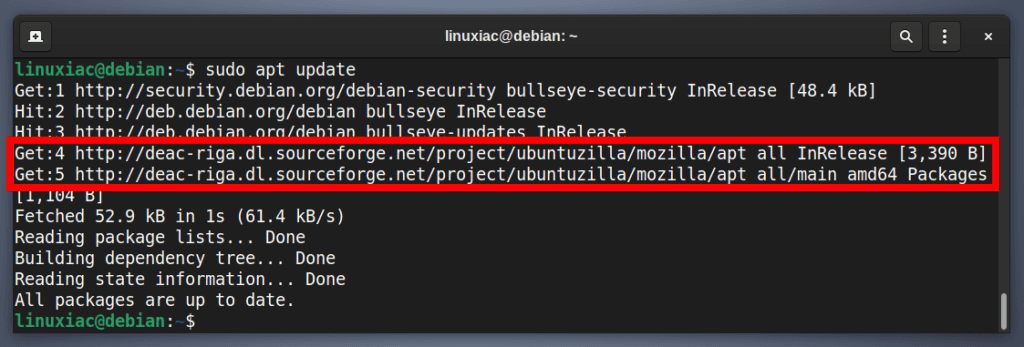
As you can see in the image above, our new Ubuntuzilla repository is now available and ready to be used.
Step 4: Install the Latest (Non-ESR) Firefox on Debian 11
To install the latest up-to-date Firefox release on Debian, run the below command.
sudo apt install firefox-mozilla-build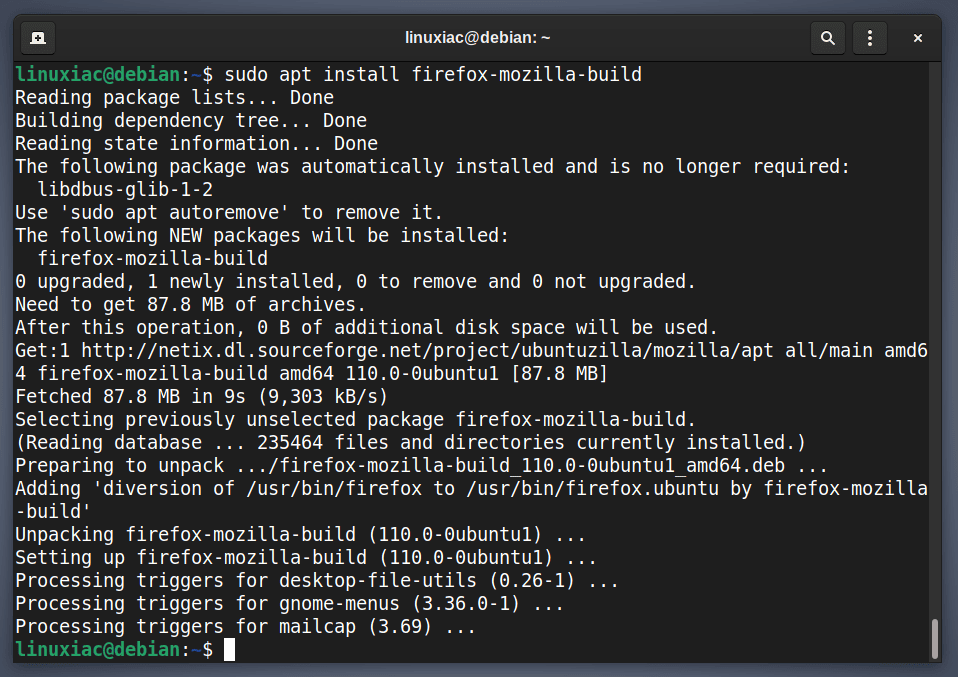
Step 5: Launch Firefox Browser
That’s all! Once installed, you can launch it from the application menu and enjoy it. Type “firefox” and click on the icon when it appears.

Firefox will start. Enjoy it!
(Optional) Uninstall Firefox
If you decide to remove the Firefox browser from your Debian system for some reason, you can do it quickly and easily by typing the command shown below:
sudo apt purge firefox-mozilla-buildMethod 2: Install Firefox on Debian 11 as a Flatpak App
Flatpak is a widely accepted and established software distribution format in the Linux world. However, Debian 11 does not come with Flatpak support by default. So if you don’t already have it installed, add it first.
sudo apt install flatpak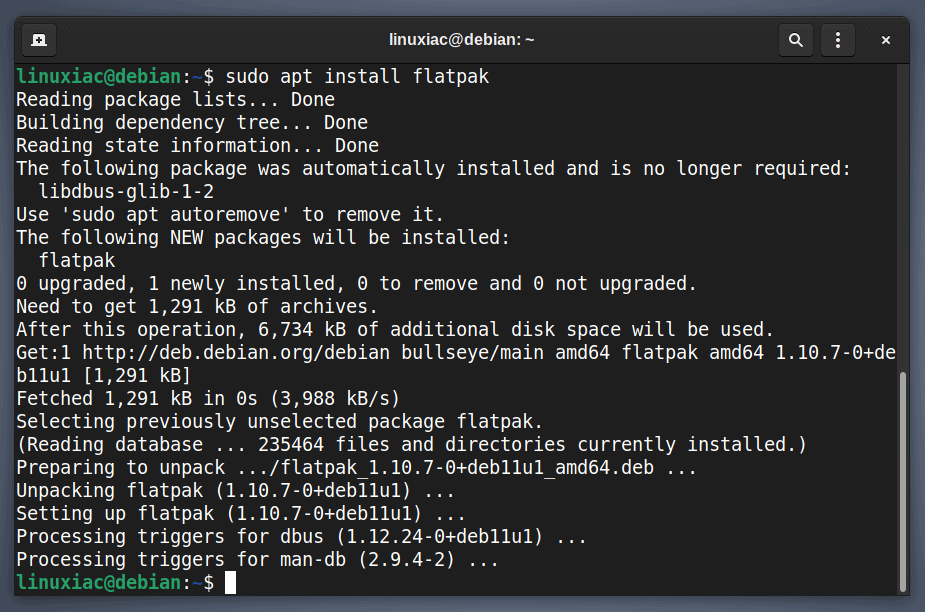
But if you’re unfamiliar with Flatpak, our excellent beginner’s guide will come in handy.
Step 1: Remove Firefox ESR
As in the previous method, remove the currently installed version of Firefox ESR first.
sudo apt purge firefox-esrStep 2: Add Flathub App Store
After installing the Flatpak runtime on your Debian 11 system, you must add the Flathub app store. Things are a lot simpler here. Run the following command in the terminal to enable the Flathub remote if it is not already enabled:
sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoCode language: JavaScript (javascript)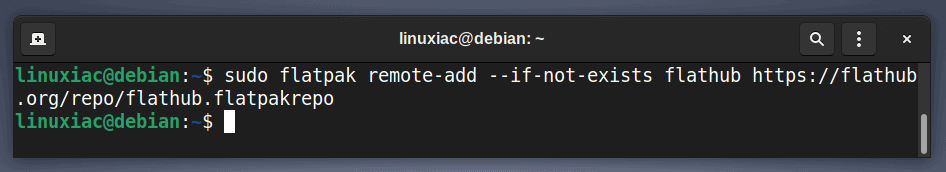
Notice that the command produces no output.
Step 3: Install the Latest (Non-ESR) Firefox as a Flatpak package on Debian 11
Finally, run the following command to install the latest Firefox release on your Debian system:
flatpak install flathub org.mozilla.firefoxCode language: CSS (css)
Next, log out and log back in. You may then launch Firefox from your current app launcher as usual.

(Optional) Remove Firefox Flatpak
If you want to uninstall the Firefox Flatpak package from your Debian 11 system, use the commands below:
flatpak uninstall --delete-data org.mozilla.firefoxCode language: CSS (css)And following best practices, free up disk space by using the following command to remove unnecessary runtime libraries:
flatpak uninstall --unusedConclusion
This brings us to the end of our guide on installing the latest non-ESR Firefox on Debian 11. Our first recommendation is to install it as a native DEB application from the Ubuntuzilla repository. The main point is that the speed is always slightly faster than the Flatpak package. However, if this looks complex, utilize the Flatpak installation method.
Of course, the choice of how to approach and what decision to make is entirely up to you. Following the steps outlined in this guide should help you easily install the latest non-ESR version of Firefox on your Debian 11 system. With it, you can enjoy the latest features, improvements, and bug fixes unavailable in the ESR version.
I hope I have been helpful to you with this guide. Any feedback is welcomed in the section below.

Hello again,
On latest Debian 11 (11.6), command you give to remove firefox-esr:
sudo apt purge firefox-esr
is not working directly as there are other packages which depend on one web browser. In a fresh debian installation (at least with xfce desktop) I could not purge firefox-esr.
One solution is, before firefox-esr purge, is to install chromium, for example, to keep at least another web browser in the system as those packages which depend on firefox-esr have an “or depend” related to some web browsers, firefox-esr and chromium included.
Regards,
Josep
Thanks for your article.
When you refer to commands:
sudo gpg –keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com –recv-keys 2667CA5C
sudo gpg -ao ~/ubuntuzilla.gpg –export 2667CA5C
cat ubuntuzilla.gpg | sudo gpg –dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/ubuntuzilla.gpg
I would add first a “cd” command in order to go to home directory for user as you are assuming it in commands.
Regards,
Josep