Solus is a unique, independently developed, rolling release distribution well known for its Budgie desktop, that belongs to the so-called original Linux distros category.
This means that it doesn’t rely on the codebases of existing Linux systems; instead, it was built from the ground up, which proudly puts it in a rather small group, along with names like RHEL, Debian, Arch, (open)SUSE, Slackware, and Gentoo.
And just like them, Solus (previously known as Evolve OS) has its own package manager called EOPKG (Evolve OS Package), which allows users to install, remove, update, and manage software packages on their systems.
Derived from the PiSi (Packages Installed Successfully as Intended) originally developed for Pardus Linux, EOPKG provides a range of functionalities, such as searching for available packages, handling dependencies, and performing system upgrades.
This guide provides everything you need, complete with easy-to-follow examples, to help you master EOPKG and confidently manage software on your Solus system. Let’s get started!
Basic Package Management
Updating the System
Keeping your system updated is crucial for security patches, bug fixes, and new features. One of the most commonly used EOPKG commands is the check for available software package updates.
sudo eopkg update-repoCode language: Bash (bash)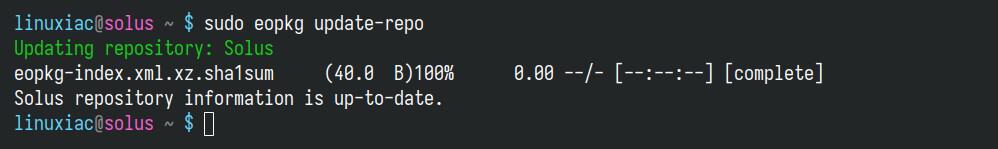
This command syncs your local package database with the remote repositories.
List Pending Updates
If you just want to view the list of packages with available updates but do not apply them to your Solus system, run the following command.
sudo eopkg upgrade -nCode language: Bash (bash)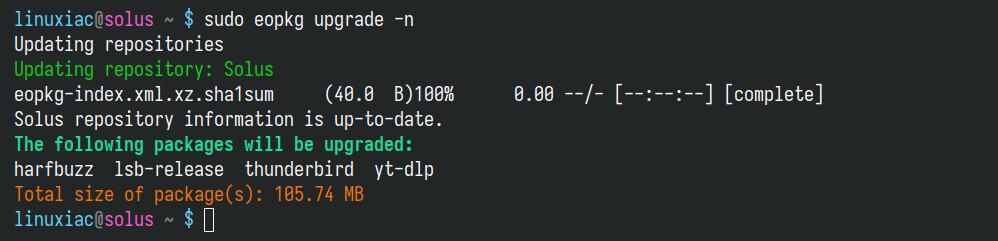
The “-n” options tell EOPKG not to perform any real upgrade actions; instead, it just shows what would be done.
Upgrade All Installed Packages
Another most commonly used action is updating operations on currently installed packages. This command updates all installed packages to their latest versions, as initially, the remote repositories will be updated to ensure all metadata is up to date.
sudo eopkg upgradeCode language: Bash (bash)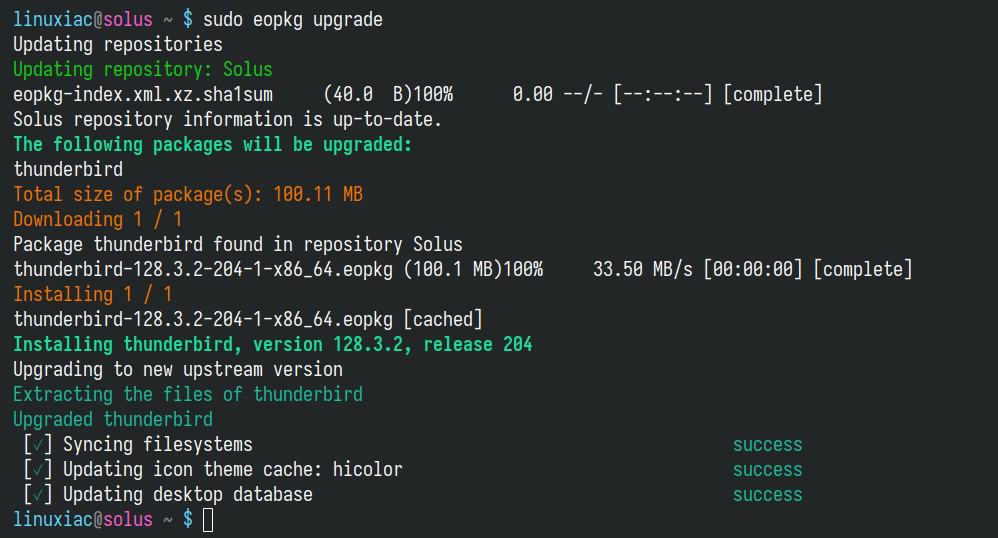
To upgrade only a specific package (or a few particular ones), just add their names after the sudo eopkg upgrade command. For example:
sudo eopkg upgrade thunderbird vimCode language: Bash (bash)Searching for Packages
A common EOPKG functionality that is widely used is packet search. For example, if we want to see whether the “firefox” package is available in the Solus software repositories, type the following command:
eopkg search firefoxCode language: Bash (bash)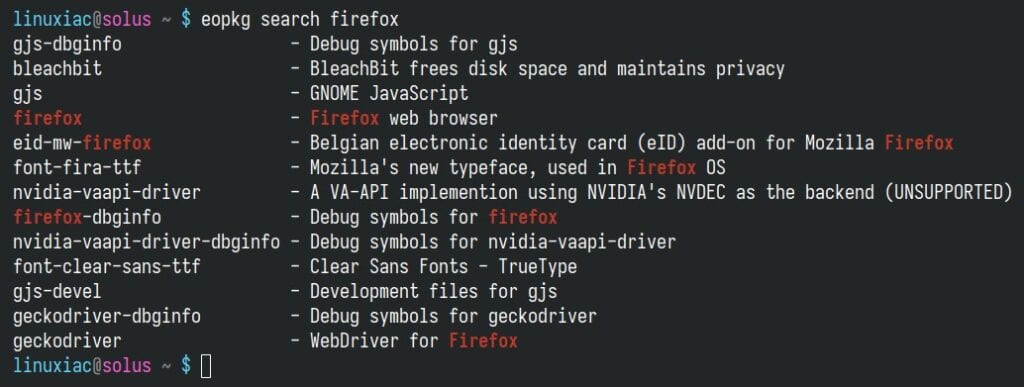
This will display a list of packages matching your search term, including the package name and description.
Searching for Already Installed Package
Sometimes, you want to check if a specific package is already installed locally. In this case, you can use the “list-installed” subcommand, which lists all installed packages, piping the output to the grep command we use to search for the specific name.
For example, to check if the “firefox” package is already installed:
eopkg list-installed | grep firefoxCode language: Bash (bash)
The command will return no result if the package is not found in the installed list.
Alternatively, you can use the eopkg info command (explained further below) and look at the first line of its output, which informs you whether the package is locally installed.
eopkg info firefoxCode language: Bash (bash)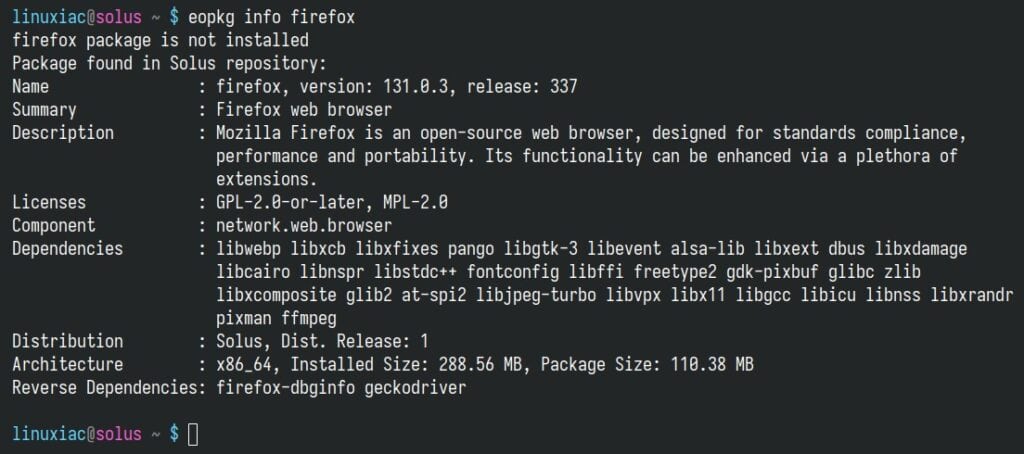
Installing Packages
Installation of a new package in Solus using the eopkg command is simple. For example, to install “firefox,” run:
sudo eopkg install firefoxCode language: Bash (bash)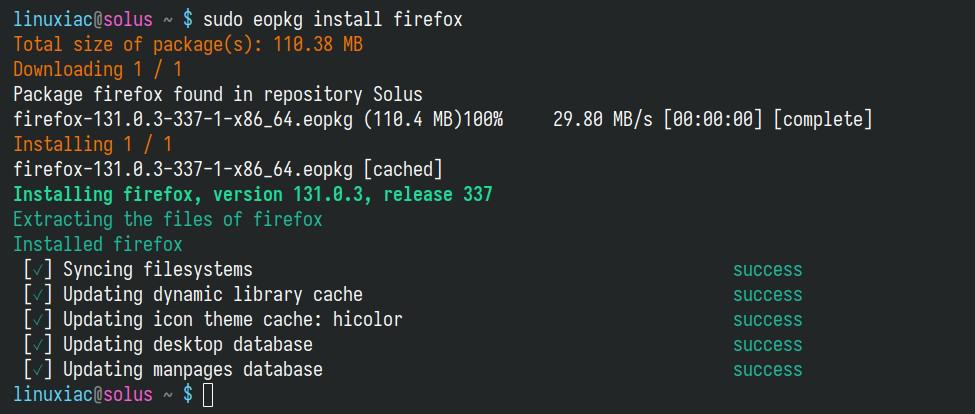
To install multiple packages on Solus, you can simply list all the package’s names one after another you want to install at the end of the command. Here’s the syntax to install, for example, Firefox, VLC, and Vim in a single run:
sudo eopkg install firefox vlc vimCode language: Bash (bash)Removing Packages
Another commonly used functionality of the EOPKG package manager is package removal/uninstallation. The remove parameter is used to uninstall software on Solus.
For example, to remove the “firefox” package from your system, you should run the following:
sudo eopkg remove firefoxCode language: Bash (bash)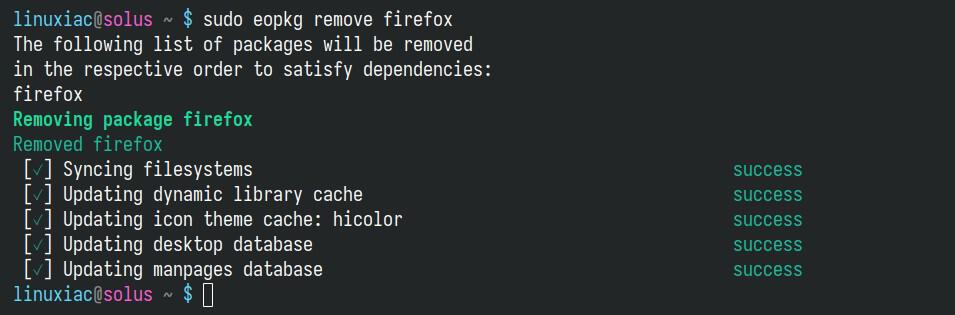
However, if you want to remove a package along with its configuration files, you can use the “–purge” option. Here’s how you can do it:
sudo eopkg remove --purge firefoxCode language: Bash (bash)Advanced Package Management
Reinstalling Packages
If an application isn’t functioning correctly, it may be due to corrupted files. Reinstalling the package can replace these files with fresh copies. Furthermore, reinstalling a package can sometimes resolve dependency conflicts or mismatches that may have occurred after a system update.
To reinstall a specific package on Solus, for example, Firefox, you can use the following command:
sudo eopkg install --reinstall firefoxCode language: Bash (bash)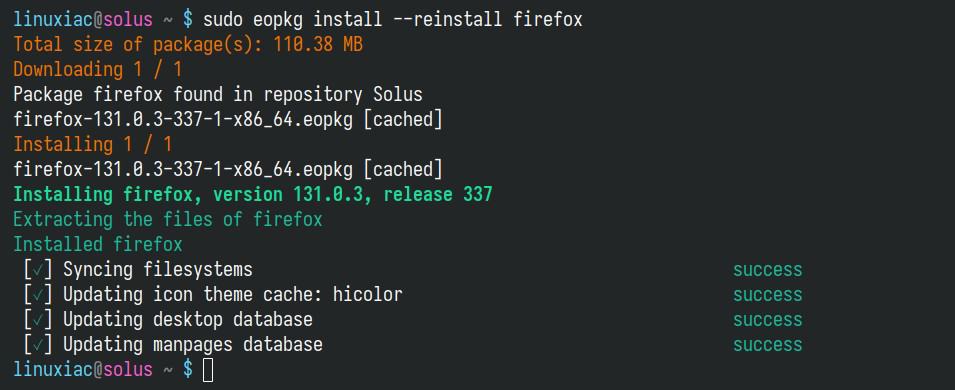
Get Information About a Specific Package
You can use the eopkg command with the “info” option to retrieve detailed information about a package (whether installed or available in the repository), including details like the package’s description, version, license, dependencies, and more.
For example, to get information about the “firefox” package, use:
eopkg info firefoxCode language: Bash (bash)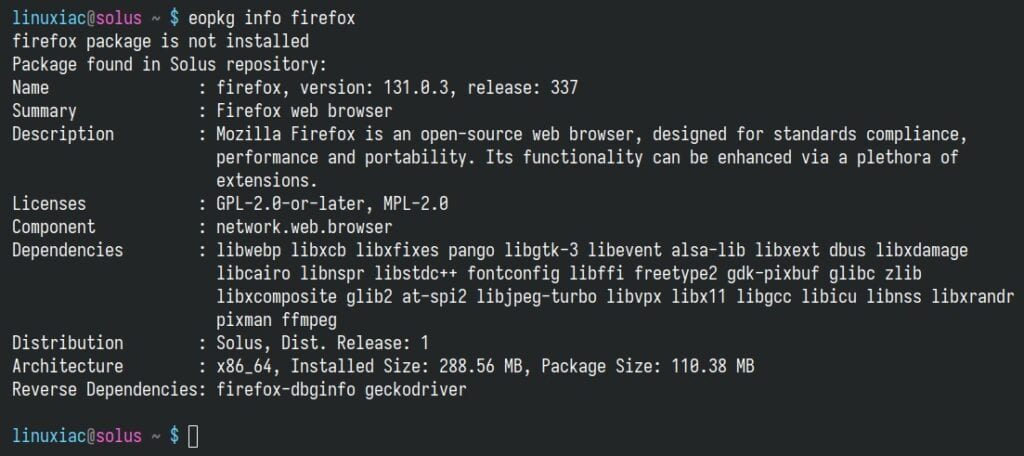
Note that if the package is already installed locally, information will be displayed for both the locally installed package and the package in the remote Solus repository.
Cleaning the Cache
EOPKG stores downloaded packages in a cache to speed up future installations and reinstallation of the same packages. However, this cache can grow large over time and consume disk space. To clear it, you can use:
sudo eopkg delete-cacheCode language: Bash (bash)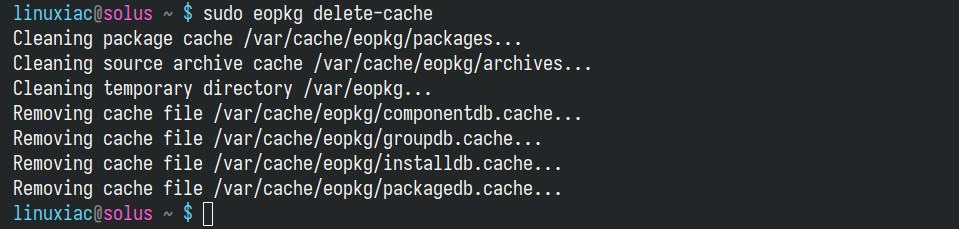
These are automatically cleared if you using the Software Centre (a GUI app for managing software on Solus). Still, if you only use the CLI approach to software management, you must manually invoke the command.
Rebuilding the Package Database
If you encounter issues with the package database, rebuilding it can help.
sudo eopkg rebuild-dbCode language: Bash (bash)
Remove Orphaned (Unused) Packages
After removing a package in Solus, some remaining orphaned (unused) packages may still depend on the removed package. However, these orphaned packages are no longer required, so we can get rid of them to free up some space.
sudo eopkg remove-orphansCode language: Bash (bash)
Rolling Back a Specific Change
The eopkg history command on Solus allows you to view a record of all package management actions performed on your system. It can be handy for rolling back specific changes, tracking updates, installations, or removals of software packages over time.
To view the package history, open a terminal and type:
eopkg historyCode language: Bash (bash)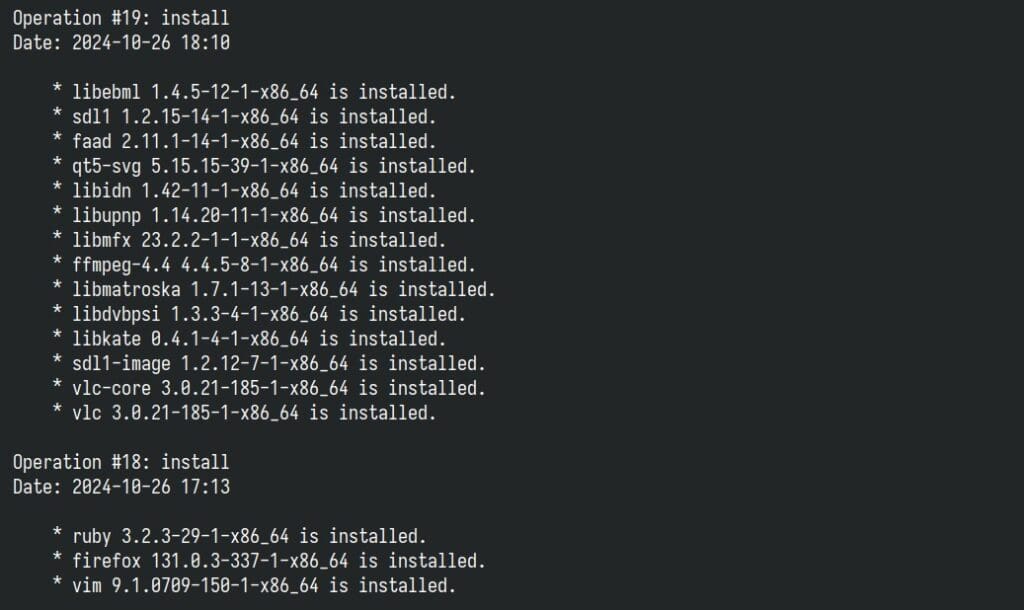
The command lists all package actions in reverse chronological order, including the action type (install, update, remove), package’s name and version, and operation’s ID.
If a recent package update caused issues, you might want to roll back to a previous state. To do this, locate the transaction ID in the history output and use it by replacing “[transaction_id]” in the example below with the actual ID with a number lower than the latest software change for the rollback action:
sudo eopkg history -t [transaction_id]Code language: Bash (bash)For example, if you want to revert the operation with an ID 19, use 18 as the number.
sudo eopkg history -t 18Code language: Bash (bash)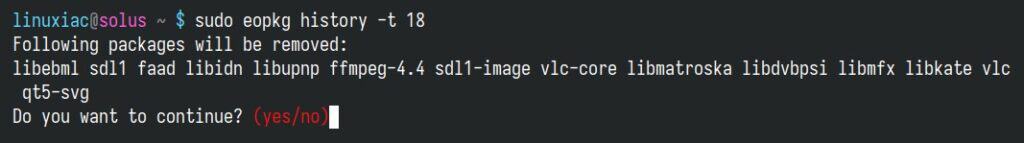
Additionally, it is important to remember that reverting software changes works if either the Solus repository has the version of the package you need or you have a local copy of the package.
Managing Repositories
Repositories are servers that store software packages, allowing users to install and update applications. Solus uses its own curated repositories by default, ensuring stability and security.
However, there might be times when you need to add additional repositories to access software that is not available in the official ones.
Listing Repositories
Knowing which repositories are currently configured on your system is useful before making changes. The command below displays a list of all repositories currently added to your Solus Linux system.
sudo eopkg list-repoCode language: Bash (bash)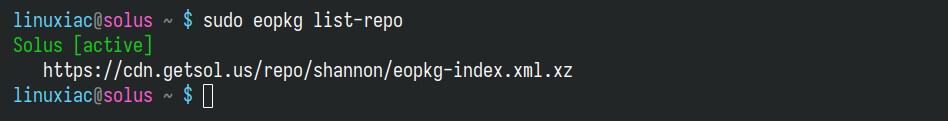
Adding a Repository
To install software from a non-official source, you must first add its repository to your system.
sudo eopkg add-repo <repository-name> <repository-url>Code language: Bash (bash)In the command above, “<repository-name>” is a label you assign to the repository. The “<repository-url>” is the URL where the repository’s packages are hosted.
Of course, once you add a new repository to your Solus system, be sure to update the package index locally on your system.
sudo eopkg update-repoCode language: Bash (bash)Remember, only add repositories from trusted sources to maintain system security.
Removing a Repository
If you no longer need a repository or it’s causing issues, you can remove it.
sudo eopkg remove-repo <repository-name>Code language: Bash (bash)Bonus Tip: Use of GUI Application
Since Solus is a desktop-focused operating system, it comes with a great graphical tool for managing software called Software Center, where with just a few mouse clicks, you can perform nearly all the tasks we’ve discussed in this guide.
However, by mastering the use of the eopkg command, you’ll significantly boost your skills and deepen your understanding of the operating system itself. So, I’m confident that once you’re comfortable with the EOPKG package manager, you’ll often prefer using it for software management in Solus.
Conclusion
We’ve reached the end of this guide. While EOPKG might not offer as much functionality and flexibility as other package managers like APT, DNF, or Pacman, it still provides everything you need to fully control the managing software on your Solus system.
With these commands at your fingertips, you can now have all the power to easily install new software, update existing applications, and maintain a clean and optimized environment without even having to touch the GUI app to do so.
Of course, the EOPKG package manager provides even more options. That said, we strongly advise you to familiarize yourself with them from the official Solus documentation.
I hope this guide was helpful in your Solus journey. As always, any suggestions and comments are highly welcome in the section below.

If anyone's old enough to remember the original Pardus distribution from the 2000's, eopkg is basically their pisi package manager with minor changes. I believe all the options discussed here were in pisi. BTW, Pardus itself moved to a Debian base long ago but its spirit lives on in a tiny Turkish distro called Pisi.
Also, it would have been helpful to note that most if not all eopkg commands have shortened versions – i.e. "it" for install, "rmo" for remove-orphans, etc. Doing "eopkg help" will give you all of them…