Less than three months after the previous 8.4 release, Redis, a distributed in-memory key-value data store, officially rolled out version 8.6, building on the foundation set by Redis 8.0.
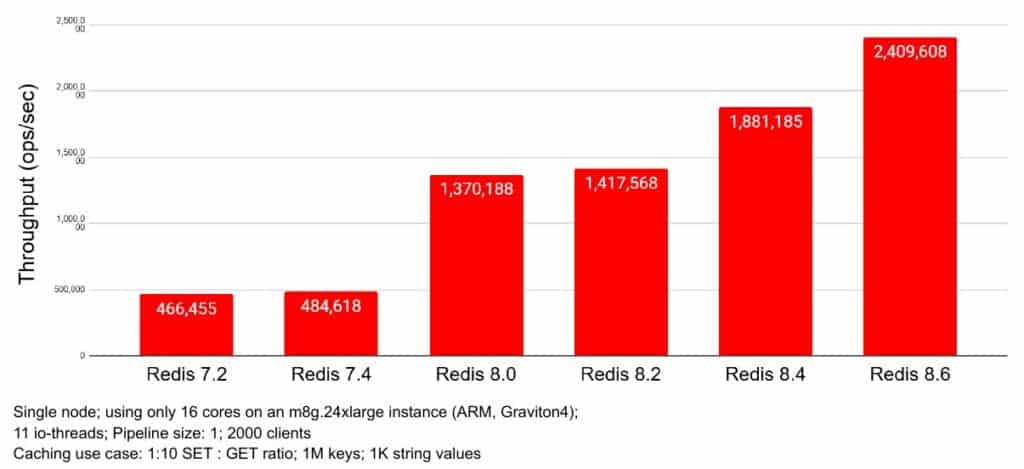
Benchmarks included with the release show throughput more than 5 times higher than Redis 7.2 in a caching workload. Additionally, with pipelining enabled, Redis 8.6 reaches up to 3.5 million operations per second.
Compared to Redis 8.4, latency is reduced by up to 35% for sorted set commands, up to 15% for GET on short strings, up to 11% for list commands, and up to 7% for hash commands. Memory usage is reduced by up to 17% for hashes and up to 31% for sorted sets.
Redis Streams now support at-most-once message delivery. Producers can attach idempotent identifiers to messages. If a message is resent after a crash or network failure, Redis detects the duplicate and does not add it to the stream again.
Two new eviction policies are introduced: volatile-lrm and allkeys-lrm. These policies evict keys based on the least-recently modified key. Read operations do not refresh recency. The volatile policy applies only to keys with expiration times. The allkeys policy applies to all keys.
Redis 8.6 adds built-in hot key detection. New commands collect CPU and network usage per key within specified hash slots. The results report the keys responsible for the highest resource consumption.
Mutual TLS authentication is simplified. Redis can automatically authenticate clients based on the Common Name in their TLS certificates. Clients no longer need to issue AUTH commands. ACL users can be configured without passwords.
Last but not least, time series support is extended to allow NaN values. TS.ADD and TS.MADD accepts NaN to mark unavailable data points. Existing aggregations ignore NaN values. New aggregators count NaN values and the total number of samples.
For more information, see the announcement. Redis 8.6 is available now via Docker Hub (Alpine or Debian images), Snap, Homebrew, RPM, and APT.
Image credits: Redis
