You sometimes need to work with disks or partitions directly from the command line on Linux. Often, you want to perform actions on the filesystems, but you do so by specifying the partitions where they are stored.
Many tools are available to find the list of currently available filesystems in Linux, the most commonly used of which is df. Unfortunately, on systems with many disks, partitions, and USB drives, it can be hard to identify the device name assigned to each of them. And this is where lfs comes on the scene.
The lfs command is used to show the amount of free disk space available on Linux and other Unix-like systems and to understand the filesystems that have been mounted. All this is shown in a clear and beautiful tabular form.
Using the lfs command is more than easy. All you need to do is to type lfs in your terminal:
lfs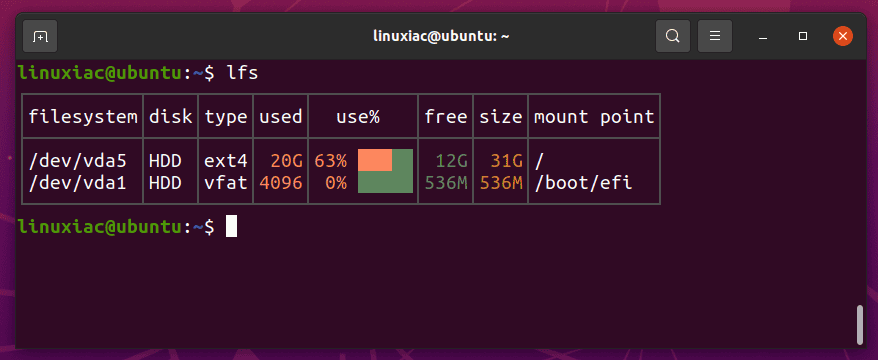
By default, lfs only lists the filesystems backed by block devices looking like real disks. You can see the other ones with the -a option.
lfs -a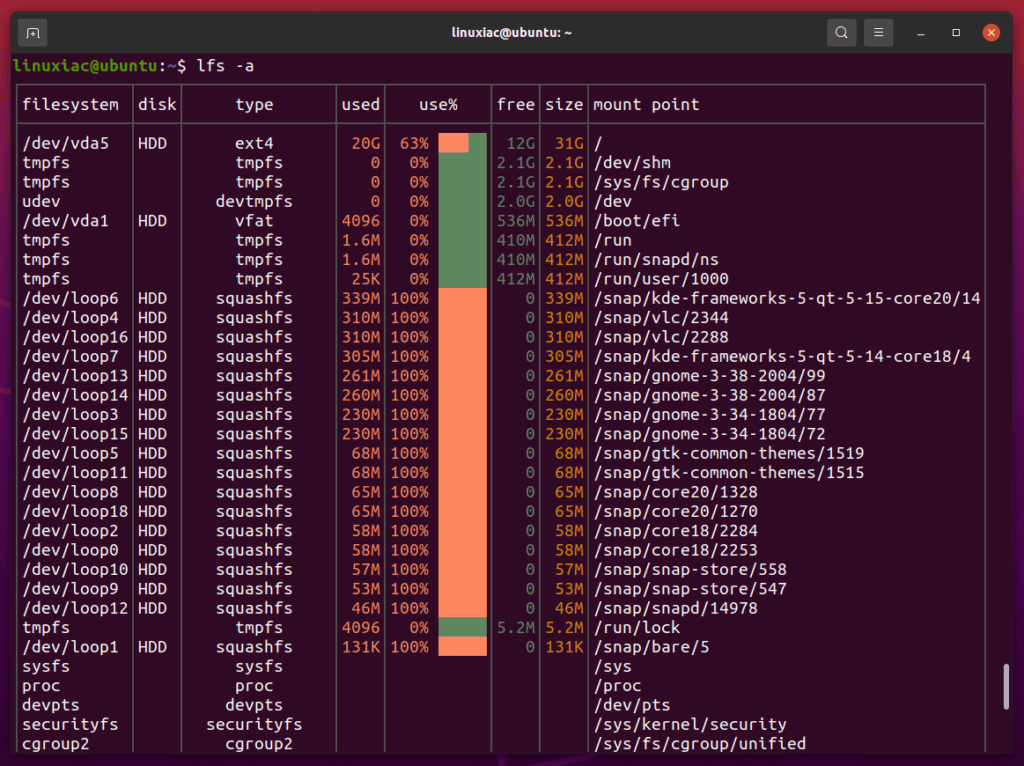
As you can see, most information given by the lfs command is already provided by df. However, there are some improvements worth mentioning:
- Helps you recognize your disks by labeling them
rem(removable),HDD, orSSD. lfsonly uses SI (The International System of Units), so you don’t have to open the help and check the right argument for the correct size units.- Displays the type of filesystem.
- Sorts filesystems by size.
For detailed information, you can refer to the project’s page.
How to Install lfs on Linux
You can download the precompiled binary from the project’s GitHub releases page.
wget https://github.com/Canop/lfs/releases/download/v2.6.0/lfs_2.6.0.zipCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Extract the zip file using the following command:
unzip lfs_2.6.0.zipCode language: CSS (css)Next, you’ll have to ensure that the shell can find the lfs executable. An easy solution is to put it in /usr/local/bin and to set it as executable:
sudo mv build/x86_64-linux/lfs /usr/local/bin/
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/lfsThat’s all. The lfs command should now be available on your system.

fyi: Followed the instructions perfectly and received this error message:
lfs: /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6: version `GLIBC_2.28′ not found (required by lfs)
I’m going to have to look into this further. System: Linux Mint 19.3