If you have forgotten the password for your MySQL database, fear not! Resetting the root password is a simple process that can be accomplished in three easy steps. So, whether you are a beginner or an experienced MySQL user, I’ll show you how to regain control of your database server.
This guide shows two different techniques for resetting the MySQL root user password. Whichever of the two you choose will give you the desired result.
Furthermore, the instruction applies entirely to the MariaDB database, a popular MySQL alternative, and, in some cases, provides additional features not available in MySQL. You can read our in-depth guide on the subject here.
Reset a MySQL root Password: The Fastest Way
To complete the steps below, you must have a local user account on the server where MySQL runs that has sudo permissions to execute privileged commands.
Step 1: Stop and Start MySQL Server without a Password
Stop the MySQL service.
sudo systemctl stop mysqldThen, as shown below, run a temporary MySQL server instance.
sudo -u mysql mysqld --skip-grant-tables &Let me explain. When the server is started with the --skip-grant-tables option, it does not read the grant tables or apply any access control. In other words, users can access it without a password.
You can now log in to the MySQL server as the root user, with no password required.
mysql -u root
Step 2: Reset a MySQL root Password
Reload the current privileges first.
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Then, reset MySQL’s root password using the following query. First, of course, replace “MyNewPassword” with the required one.
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPassword';Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Finally, reload the privileges one more time and exit.
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
quit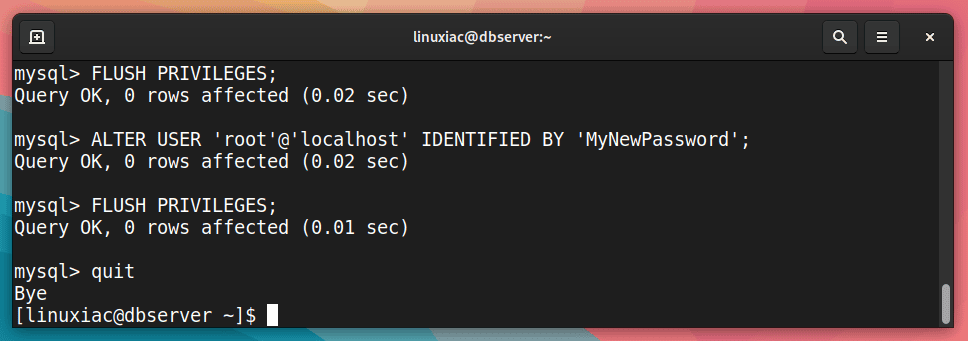
If you want to learn more about adding users to MySQL and providing them with privileges, here’s our guide.
Step 3: Restart and Connect to the MySQL Server
Now that we’ve changed the password, you need to stop the temporarily running MySQL server by finding its process number and terminating it. You can easily accomplish this with the following command:
ps auxw | grep '\-\-skip-grant-tables' | tail -n 1 | awk '{ print $2 }' | sudo xargs kill
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Then restart the MySQL server and log in with the new password.
sudo systemctl start mysqld
mysql -u root -p
Congratulations! The MySQL server is now back in your control.
Reset the MySQL’s Root Password by an Initialization File
To complete the steps below, you must have a local user account on the server where MySQL runs that has sudo permissions to execute privileged commands.
Step 1: Switch to the mysql System User and Stop the MySQL Server
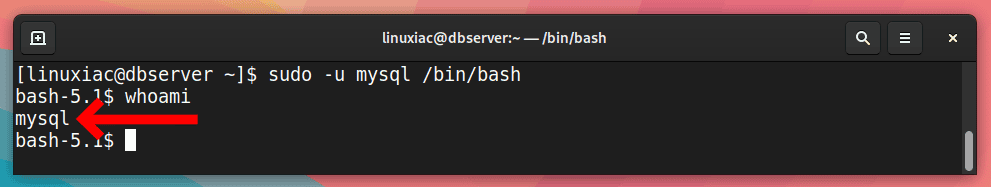
To complete the steps below successfully, you must switch to the system user account that runs your MySQL server. This is typically the system account with the username mysql. To switch to it, run the following:
sudo -u mysql /bin/bashYou can use the whoami command to ensure that you work with the correct user.
Then, stop the MySQL server passing the kill command the full path to the PID file holding the process number with which it started. If you’re not sure where this file is, you can quickly locate it by running the following:
mysqld --print-defaults | tr " " "\n" | grep pid | tail -n 1Code language: PHP (php)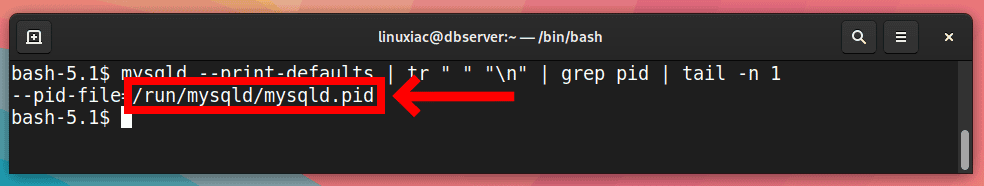
Finally, stop the MySQL server.
kill `cat /run/mysqld/mysqld.pid`Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Step 2: Create a MySQL Password Reset File
Using your preferred text editor in the /tmp directory, create a text file named “mysql-init.txt,” with a single line containing the password-assignment query.
vim /tmp/<em>mysql-init.txt</em>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Insert the following line, being sure to change the password to the one you want to use.
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPassword';Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Save the file and exit.
Step 3: Start MySQL Server
Start the MySQL server as shown below, with the --init-file option set to the full path to the file you just created.
mysqld --init-file=/tmp/mysql-init.txt &Code language: JavaScript (javascript)That’s all. The MySQL root user’s password has been changed, and you can now log in as root with the password you specified in the file above.
mysql -u root -p
You can now safely delete the “/tmp/mysql-init.txt” file. You don’t need it anymore.
Conclusion
As you can see, resetting the MySQL root password is a relatively simple process that can be accomplished in three steps. However, it is essential to note that resetting the root password should only be done as a last resort, as it can potentially expose your database to security risks.
Therefore, it is always a good idea to carefully manage your password and keep it secure to avoid resetting it in the future. You can find additional information in the official documentation.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to comment.

There are countless solutions, but this is the only one that worked for me (MySQL on Almalinux). Thank you so much.