This guide is for users running Docker on AlmaLinux 8 or Rocky Linux 8. If you’ve already upgraded to Alma 10 or Rocky 10, check out our updated guides — you can find the one for Alma 10 here and the one for Rocky 10 here.
Docker is a popular open-source platform for developing, deploying, running, and shipping container applications. They are similar to virtual machines and help separate applications from the underlying system.
If you’ve just installed AlmaLinux 8 or Rocky Linux 8, you may be wondering how to get Docker up and running, as RHEL doesn’t offer native support for Docker.
It probably seems strange to you, and if you ask yourself if there is a reason for this, the answer is yes, there is. Red Hat supports its product, Podman, an alternative to Docker.
So without further ado, let me show you how to install Docker on AlmaLinux or Rocky Linux and get started with installing containerized software.
Step 1: Updating the System
Begin by updating the AlmaLinux 8 / Rocky Linux 8 system OS packages to recent versions. This way, we ensure we have a wholly upgraded system.
So, first, please update existing software with the following command:
sudo dnf updateCode language: Bash (bash)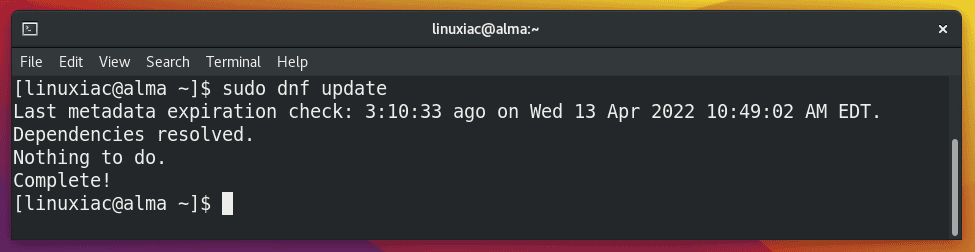
As you can see, no update packages are available, but if you have updates, apply them before proceeding to the next step.
Step 2: Adding Docker Repository
A Docker repository for RHEL-based Linux systems contains RPM packages for installation. So we’ll need to add this repository before installing Docker.
First, type the following command in your terminal window to install the yum-utils package:
sudo dnf install yum-utilsCode language: Bash (bash)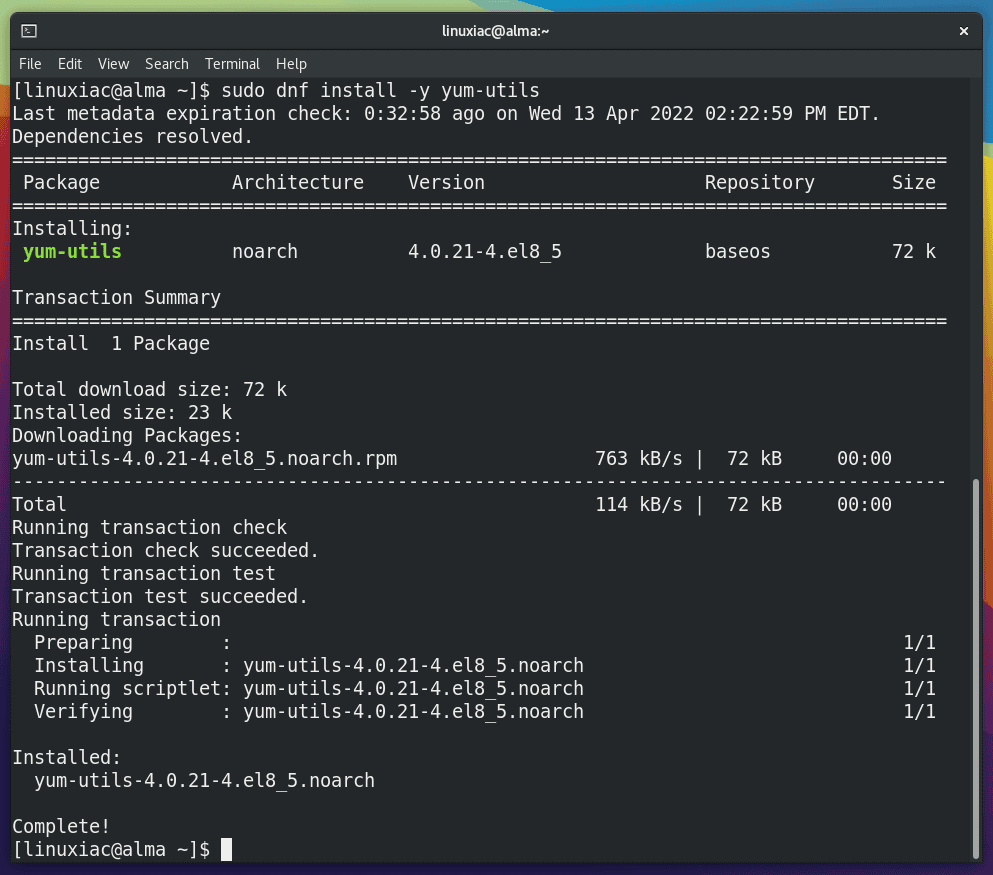
The yum-utils package provides a collection of tools for managing yum repositories.
Next, we need to add the Docker repository to our system with the following command:
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repoCode language: Bash (bash)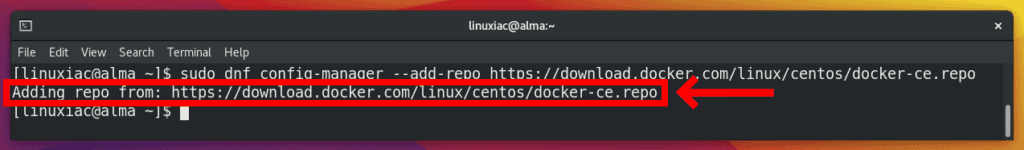
As you can see, the system informs you that it has successfully retrieved the repository.
Step 3: Run System Update
Run the system update, forcing your Alma / Rocky installation to rebuild the system repo cache to recognize the newly added Docker repository and its packages.
sudo dnf updateCode language: Bash (bash)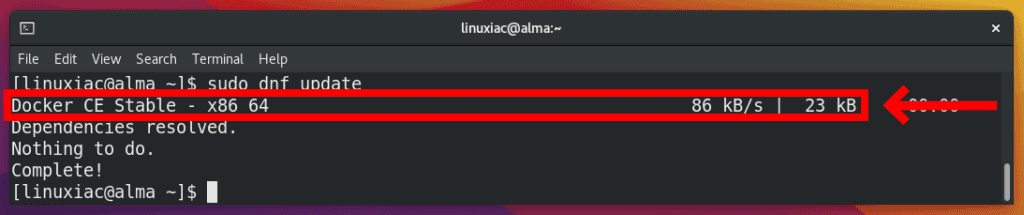
Step 4: List Available Repos
You can use this command to verify that the Docker repo was properly added:
sudo dnf repolistCode language: Bash (bash)
Step 5: Install Docker on AlmaLinux 8 / Rocky Linux 8
Now that we’ve added the Docker repository to our system, we can install Docker along with its command-line tool and containerd.io to manage the container lifecycle of our host system more efficiently.
The command below will install the latest Docker package for Alma 8 / Rocky 8:
sudo dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.ioCode language: Bash (bash)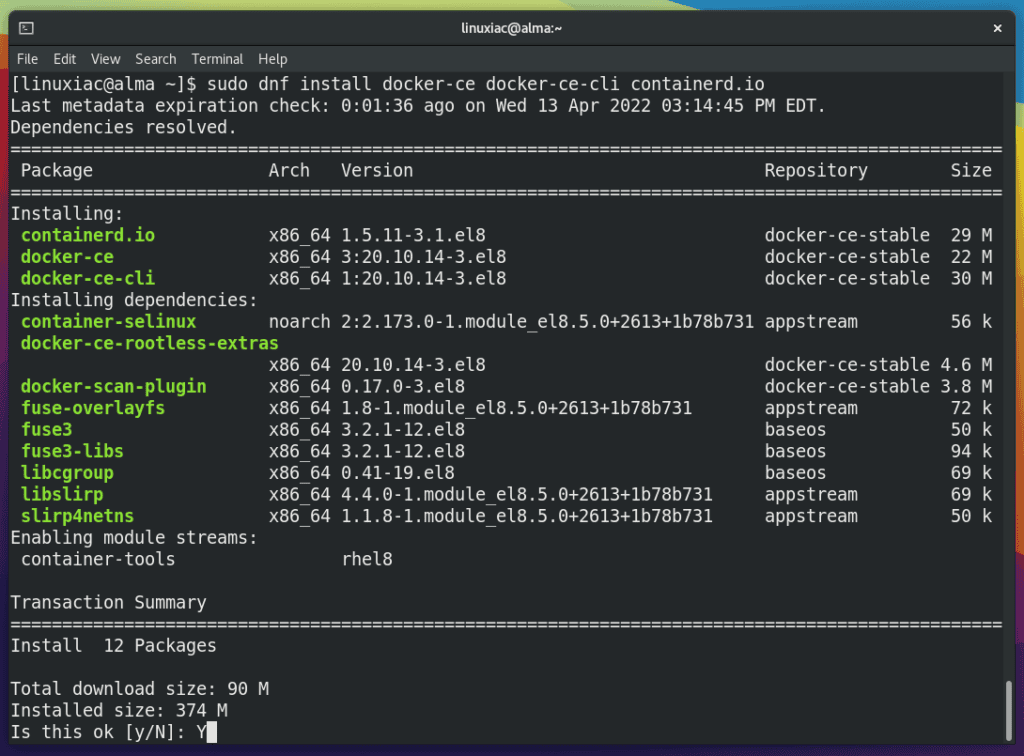
Confirm with “Y” that you allow the installation of the displayed list of packages.
Next, you will be asked if you accept the Docker GPG key to be imported into your system. Confirm again with “Y.”
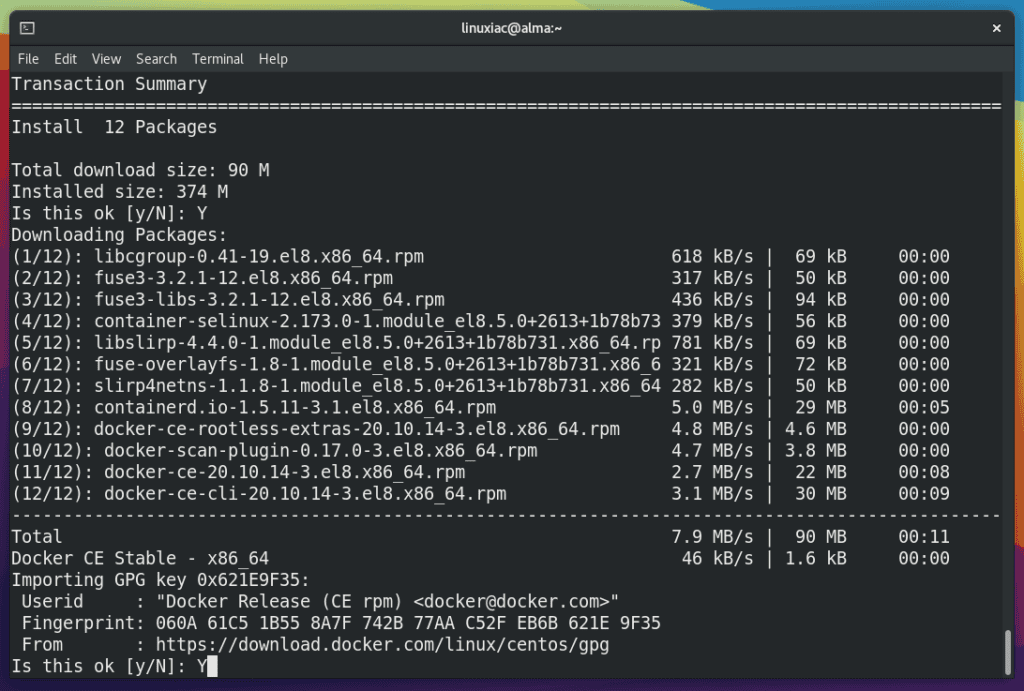
Wait for the confirmation message for the successful completion of the Docker installation on your AlmaLinux / Rocky Linux system.
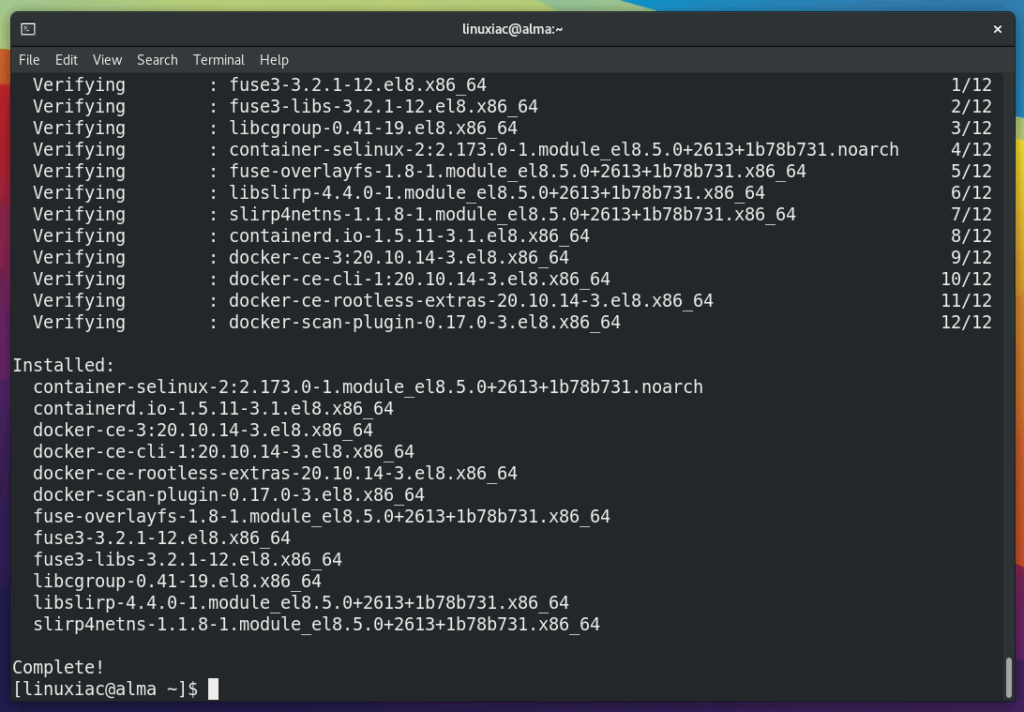
Step 6: Start, Enable, and Verify the Docker Service
After the installation is complete, you can launch the Docker service and configure it to start automatically when the system boots:
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable dockerCode language: Bash (bash)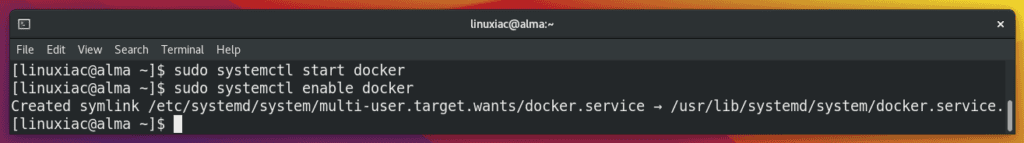
To confirm the running status of Docker, issue the command:
sudo systemctl status dockerCode language: Bash (bash)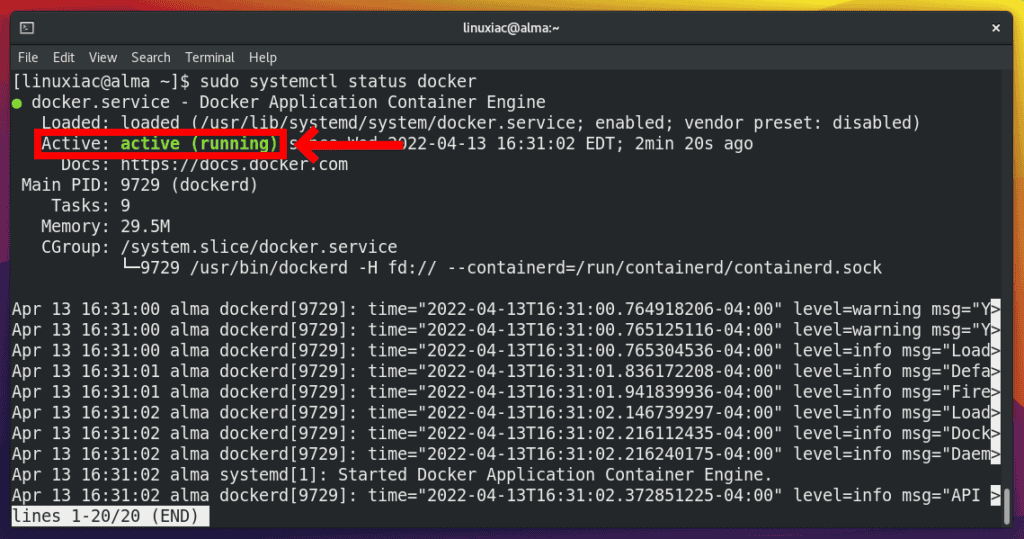
As you can see, Docker is up and running as expected.
Step 7: Enabling Non-root Users to Run Docker Commands
So far, we have successfully installed Docker on our AlmaLinux / Rocky Linux system.
However, only root and users with sudo privileges can execute Docker commands by default. So, if you attempt to run the docker command without prefixing it with sudo, you’ll get an output like this:
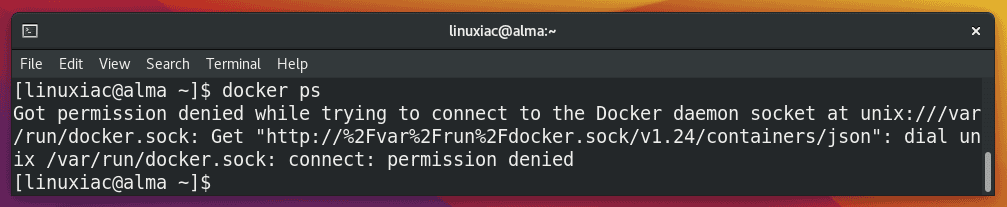
To run Docker commands as a non-root user, you must add your user to the docker group. To do that, type in:
sudo usermod -aG docker ${USER}Code language: Bash (bash)In the command shown above, ${USER} is an environment variable that holds your username.
Now, you can check if your user is in docker group or not:
id $USERCode language: Bash (bash)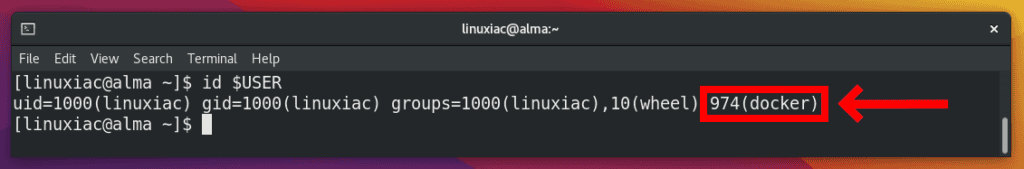
You can log out and log back in to get the group membership session updated.
Step 8: Testing the Docker Installation
Now that we’ve installed Docker on AlmaLinux / Rocky Linux, it’s time to ensure everything is working correctly.
To do this, we’ll need a container image to test with. Fortunately, an image is already available for testing. Let’s put the installation to the test by running the hello-world container with the following commands:
docker pull hello-world
docker run hello-worldCode language: Bash (bash)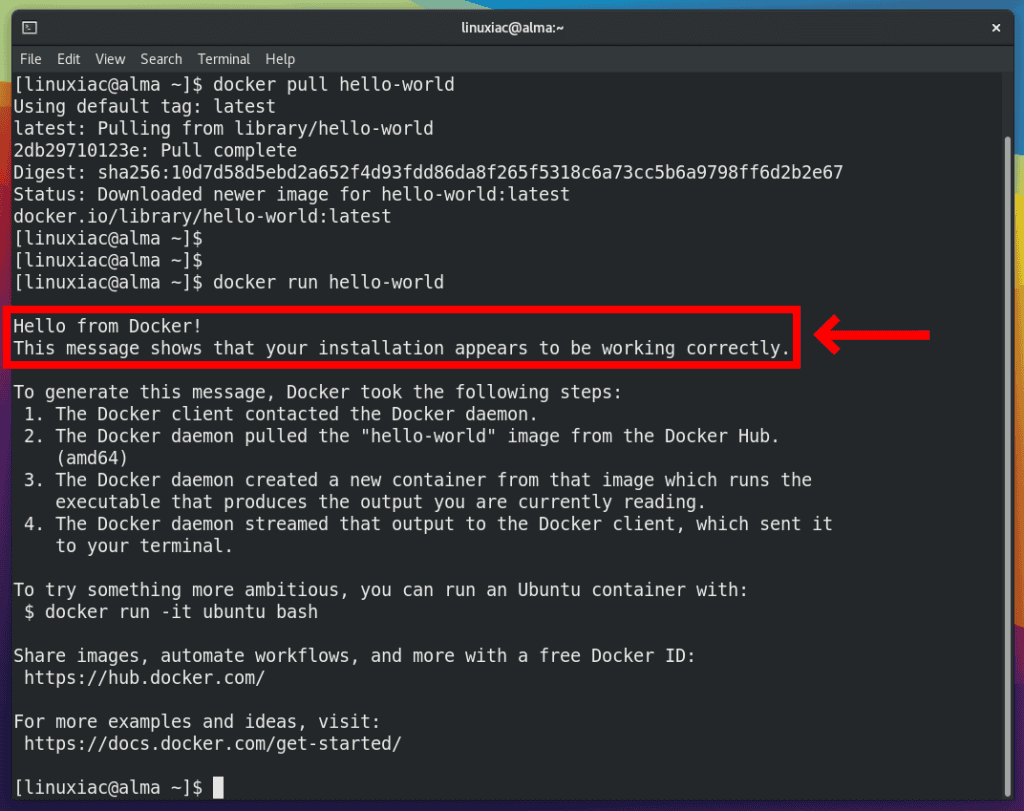
Congratulations! You deserve it. This output confirms that the installation of Docker on AlmaLinux 8 / Rocky Linux 8 was successful.
Conclusion
This tutorial demonstrated installing Docker on an AlmaLinux 8 / Rocky Linux 8 system. Now you can get started with pulling images and running containers.
To learn more about Docker, check out the official Docker documentation or look at our introductory guide: What is a Docker Container: An Introductory Guide for Beginners.
If you have any questions or suggestions, let me know, and I’ll be happy to follow up with you. Happy docking!
