Over three months after the previous 8.2 release, Redis, a distributed in-memory key-value data store, officially rolled out version 8.4, building on the foundation set by Redis 8.0.
The headline feature is the new FT.HYBRID command, which brings full-text and vector search together in a single query path. Previous approaches required multi-step logic, manual score merging, or external pipelines, all of which increased latency and reduced precision.
This allows applications to express intent more naturally, mix semantic and literal matching, prioritize recent context, and incorporate GEO and GEOSHAPE filters.
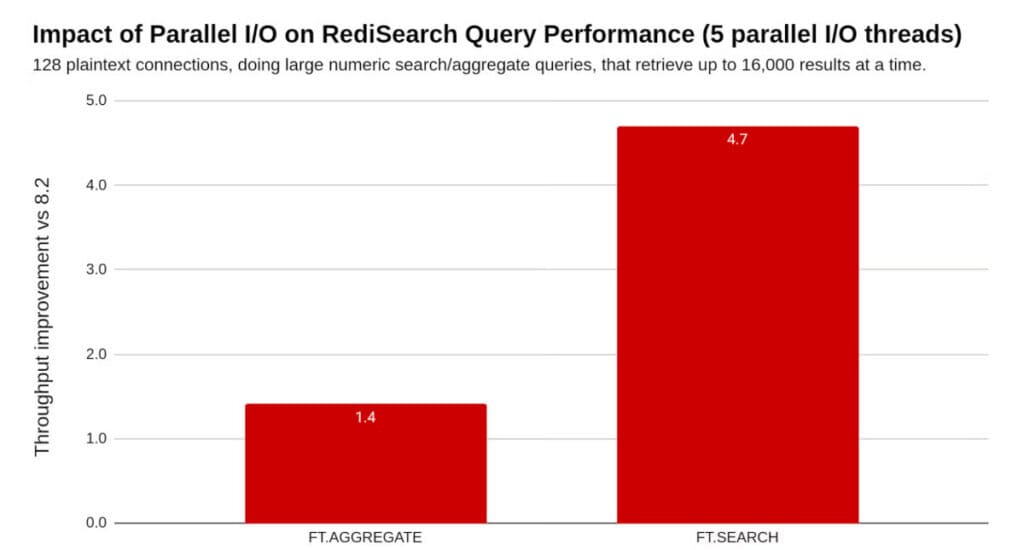
On the performance side, according to devs, Redis 8.4 delivers more than 30% higher throughput for typical caching scenarios—90% GET and 10% SET—compared to Redis 8.2. Search workloads also see gains due to the introduction of multi-threaded I/O processing for distributed queries.
When large result sets are spread across multiple shards, responses are now handled concurrently instead of being funneled through a single thread. Aggregate operations benefit as well, reducing response times and keeping worker threads free to perform search and scoring logic.
Regarding Memory efficiency, Redis 8.4 further reduces JSON memory consumption by optimizing the storage of short strings and homogeneous numeric arrays. Short strings of up to seven bytes are now inlined, cutting memory use by roughly 37% in common cases.
Large numeric arrays benefit even more. By storing the element type once per array and selecting the most compact safe representation—int, uint, BF16, FP16, FP32, or FP64—the engine can reduce memory usage by 50% to 92%, depending on the value range.
Moreover, the release also adds new atomic operations that previously required Lua scripting. String keys now support compare-and-set and compare-and-delete directly through new SET options (IFEQ, IFNE, IFDEQ, IFDNE) and the new XDELEX command. Multi-key updates also become easier with MSETEX, which can set multiple keys and conditionally manage their expiration conditions in a single operation.
Last but not least, cluster deployments see major improvements through Atomic Slot Migration. Earlier Redis versions migrated slots key by key, resulting in redirects, broken pipelines, inconsistent multi-key operations, and potential data loss in failure scenarios.
Atomic Slot Migration instead transfers an entire slot’s data and its ongoing changes to the destination node before performing a single ownership handoff. Clients continue interacting with the source node during the copy, helping avoid mid-migration errors and reducing operational risk.
For more information, see the announcement. Redis 8.4 is available now via Docker Hub (Alpine or Debian images), Snap, Homebrew, RPM, and APT.
Image credits: Redis
