As you know, Linux is a multi-user system, which means that more than one user can interact with the same system simultaneously. Therefore, user management is an essential part of Linux administration.
You’re probably already familiar with adding new users in Linux. So let’s now learn how to remove them.
userdel Command Syntax
The userdel command in Linux is a low-level utility used to remove a user account and related files. The command modifies the system account files, deleting all entries that refer to USERNAME.
userdel [OPTIONS] USERNAMECode language: CSS (css)The command has only a few options, the most significant three of which are listed below:
| Option | Explanation |
|---|---|
| -r | Files in the user’s home directory will be removed along with the home directory and the user’s mail spool. Files owned by the user in other file systems will have to be searched for and deleted manually. |
| -f | Forces the removal of the user account, even if the user is still logged in. It also forces userdel to remove the user’s home directory and mail spool, even if another user uses the same home directory or if the specified user does not own the mail spool. |
| -Z | Remove any SELinux user mapping for the user’s login. |
The exact syntax applies to any Linux distribution. To remove users using the userdel command in Linux, you need to be logged in as root or as a user with sudo privileges.
Remove User in Linux
For example, if you want to remove a user “john” from your Linux system, enter:
sudo userdel johnRemember that the userdel command won’t work if the user is logged in or has processes running under the account. Instead, you will get a message similar to the one displayed below.
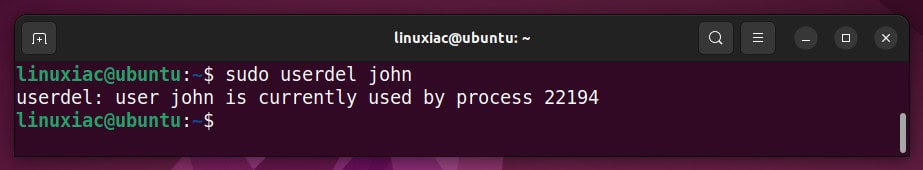
In this case, you must use the -f option to force deletion.
sudo userdel -f johnRemove User along with Their Home Directory in Linux
When you run a userdel command without any options specified in the command line, the user’s home directory and mail spool will remain in the system.
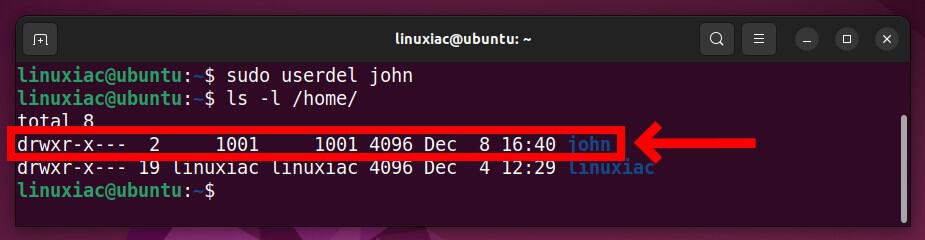
To remove the user “john” along with its home directory and mail spool, execute the userdel command with the -r option.
sudo userdel -r john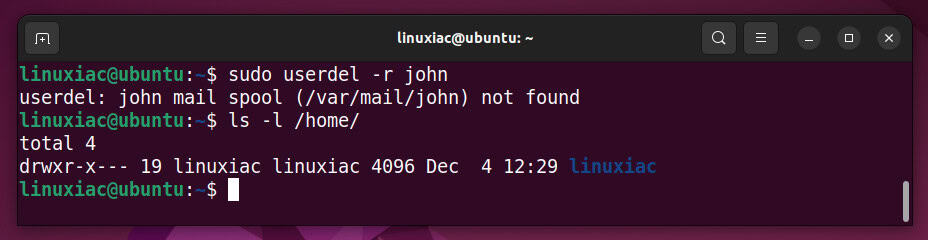
The command will remove files in the user’s home directory, the home directory, and the user’s mail spool. Please note that the user’s files in other filesystems will have to be searched for and deleted manually.
Find Files Left by the User After Deletion
However, even if you use the -r option to delete a user in Linux, there may be leftover files in the file system that no longer have an owner. Therefore, it is best practice not to leave files that do not have an owner or group assigned to them.
You will need the user’s UID and GID to find files owned by them. Therefore, before running the userdel command, double-check that you have written the user’s UID and GID somewhere on the side. You can easily find them using the id command followed by the user name.
id john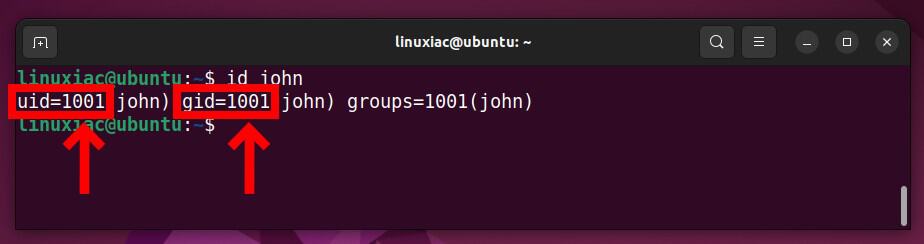
Once you know the user’s UID and GID, you can delete the user. Then, use the find command to search the entire file system for any leftover files owned by the removed user.
sudo find / -uid 1001 -gid 1001 -exec ls -l {} \;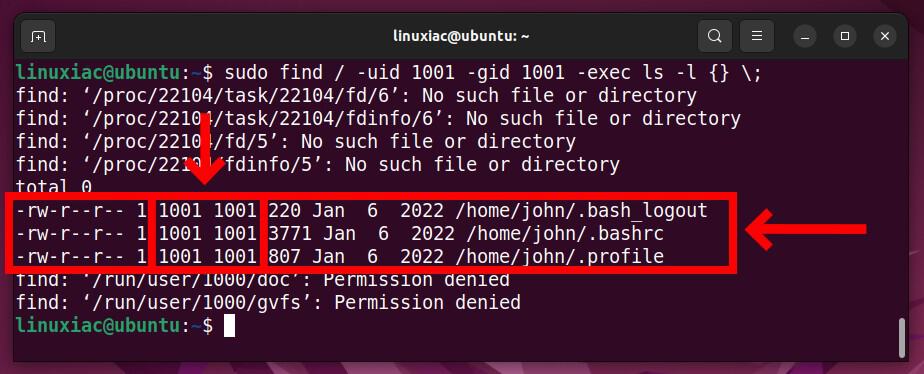
For more detailed information about the userdel command, you can head to the command’s man page.
Conclusion
This guide shows you how to remove a user from a Linux system using the userdel command. We also showed you how to find and delete any leftover files still owned by the deleted user.
We hope we were of help to you. Any feedback and suggestions are very welcome in the comments section below.

So what happens if one does “userdel -f root” ?
you will be doomed