You can easily keep your system’s date and time accurate by using NTP (Network Time Protocol). It lets you synchronize computer clocks through network connections and keep them accurate. A client requests the current time from a remote server and uses it to set its clock.
How to Synchronize Time with NTP Using systemd
The majority of Linux distributions have adopted systemd, and with it comes the systemd-timesyncd daemon.
That means you have an NTP client already preinstalled, and there is no need to run the full-fledged NTPD daemon anymore. Instead, the built-in systemd-timesyncd can do the primary time synchronization job fine.
To check the current status of time and time configuration via timedatectl, run the following command:
timedatectl status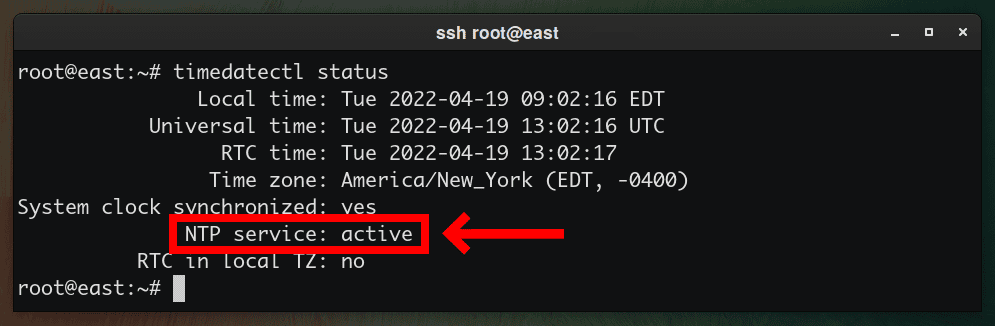
If you see NTP service: active in the output, your computer clock is automatically adjusted through NTP.
If you see NTP service: inactive, run the following command to enable NTP time synchronization.
timedatectl set-ntp trueCode language: JavaScript (javascript)That’s all you have to do. Everything should be in place once that’s done, and time should be kept correctly.
In addition, timesyncd itself is still a normal service, so you can also check its status more in detail.
systemctl status systemd-timesyncd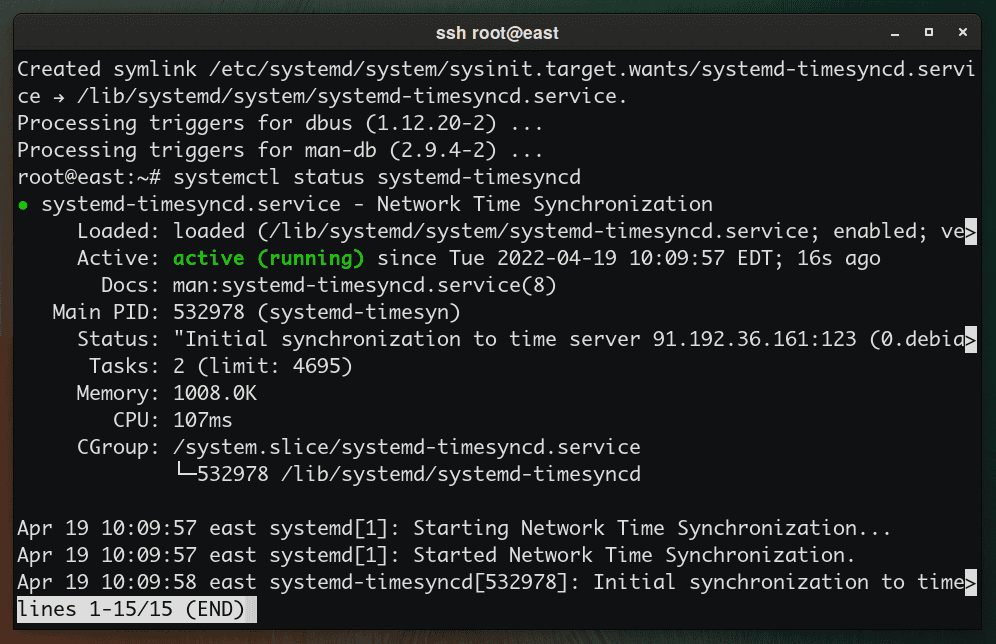
If it is disabled, you can start and make the systemd-timesyncd service active like this:
systemctl start systemd-timesyncd
systemctl enable systemd-timesyncdHow to Set/Change Timezone on Linux
Before changing your time zone, start using timedatectl to determine the currently set time zone.
timedatectl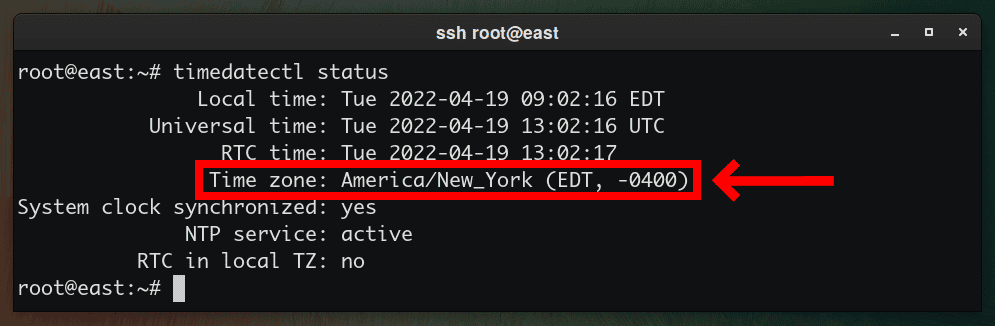
Now let’s list all the available time zones, so you know the exact name of the time zone you’ll use on your system.
timedatectl list-timezonesCode language: PHP (php)
The list of time zones is quite extensive. First, however, you need to know the official timezone name for your location.
Another way to find your timezone is to list (ls -l) the contents of the /usr/share/zoneinfo/ directory. Find your preferred timezone (/usr/share/zoneinfo/Zone/SubZone) where Zone/SubZone is your selection, such as America/New_York, Europe/Paris, Asia/Bangkok, and so on. You got the idea.
Say you want to set the timezone on your Linux system to New York. The command should be like this:
timedatectl set-timezone America/New_YorkCode language: JavaScript (javascript)This command creates a symbolic link for the time zone you choose from /usr/share/zoneinfo/ to /etc/localtime.
In addition, you can skip the command shown above, create this symbolic link manually and achieve the same result.
ln -s /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/New_York /etc/localtimeHere’s the man page for the timedatectl command if you need it.

So that’s it? No ntpd help at all? Only the systemd way?
Yes, systemd-timesyncd is enough to do all the work. In fact, it implements an SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) client.
But very helpful if you do!!!
Not helpful if you don’t use systemd